
 |
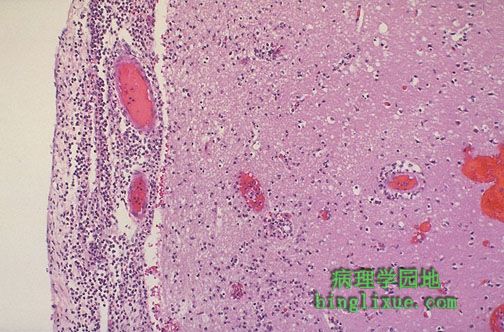
显微镜下,左侧受累的脑膜上可见嗜中性粒细胞渗出,并有明显的血管扩张。在通向右侧的皮质处有水肿和局部炎症(经由菲-罗隙向下扩展)。急性脑膜炎多为细菌感染。水肿可引起脑疝和死亡。感染的溶解可能引起粘连性蛛网膜炎,粘连性蛛网膜炎使蛛网膜下腔变小甚至消失,最后造成梗阻性脑积水。 Microscopically, a neutrophilic exudate is seen involving the meninges at the left, with prominent dilated vessels. There is edema and focal inflammation (extending down via the Virchow-Robin space) in the cortex to the right. This acute meningitis is typical for bacterial infection.This edema can lead to herniation and death. Resolution of infection may be followed by adhesive arachnoiditis with obliteration of subarachnoid space leading to obstructive hydrocephalus. |
|||||||||||||||
|
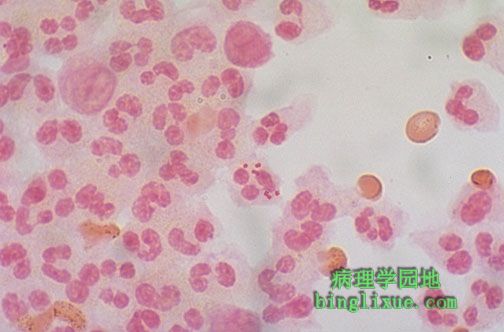
显微镜下,中性粒细胞内可见的革兰氏染色阴性的双球菌,为脑膜炎奈瑟球菌。腰穿抽取脑液可进行革兰氏染色和细菌培养。许多细菌都可能引起脑膜炎,但是几种最常见,并且特定的年龄段发生的机率更大。如大肠杆菌、嗜血流感杆菌、脑膜炎奈瑟菌、肺炎链球菌。 Microscopically, a gram stain reveals gram negative diplococci within a neutrophil, typical for Neisseria meningitidis. Gram stain and culture can be performed on cerebrospinal fluid obtained via lumbar puncture. A variety of bacteria can cause meningitis, but several are more common, and have an incidence more frequent at certain ages: |
|||||||||||||||
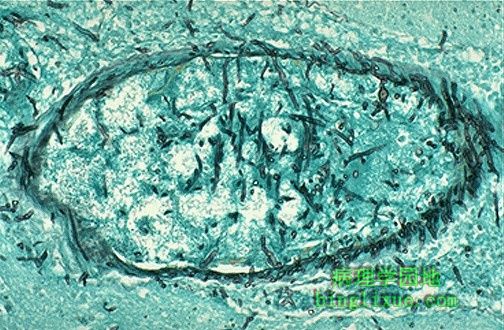 |
传播感染可见于免疫受损病人,这种类型的感染包括真菌。图示曲霉菌的分枝状菌丝正侵入脑血管。曲霉菌趋于侵入血管,导致出血和血栓。 Disseminated infections can be seen in immunocompromised hosts. Such infections can include fungi. Seen here are branching hyphae of Aspergillus invading a cerebral vessel. Aspergillus likes to invade vessels and produce hemorrhage and thrombosis. |
|||||||||||||||
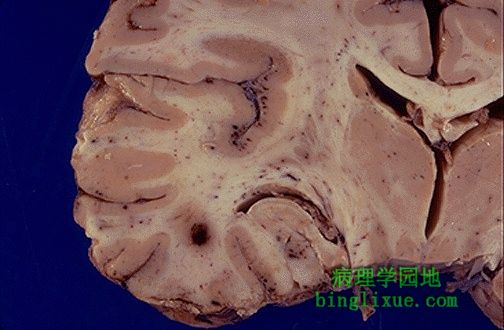 |
单纯疱疹病毒感染致颞叶出血。显微镜下,病毒感染引起单核细胞浸润。 The hemorrhages seen here in the temporal lobe are due to Herpes simplex virus infection. Viral infections produce mononuclear cell infiltrates microscopically. |
|||||||||||||||
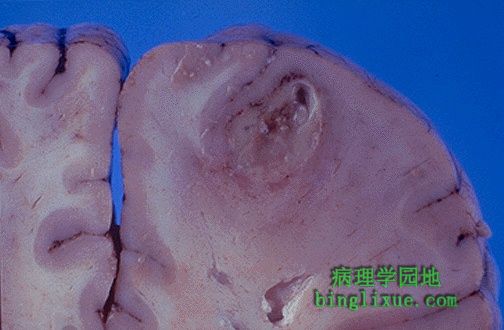 |
脑脓肿,可见薄壁并附有黄色脓液的液化中心。脓肿通常由以下原因引起:细菌感染后通过血液播散、直接贯通伤、临近血窦感染的播散。 This is a cerebral abscess. There is a liquefactive center with yellow pus surrounded by a thin wall. Abscesses usually result from hematogenous spread of bacterial infection, but may also occur from direct penetrating trauma or extension from adjacent infection in sinuses. |
|||||||||||||||
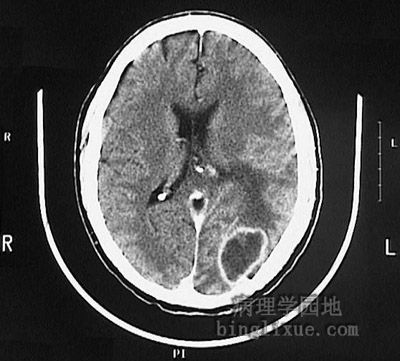 |
CT显示败血症病人脑脓肿。 This computed tomographic (CT) scan of the head in transverse view demonstrates an abscess in the brain in a patient who had septicemia. |
|||||||||||||||
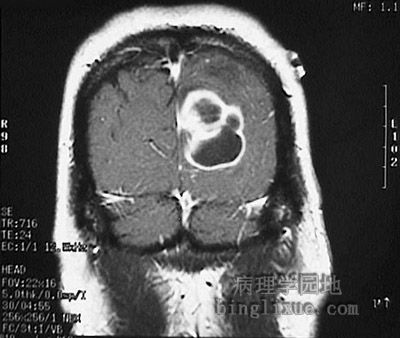 |
MRI显示大的多腔的脑脓肿(矢状面)。 The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the head seen below in sagittal and axial views demonstrate a large multiloculated abscess in the brain. |
|||||||||||||||
 |
MRI显示大的多腔的脑脓肿(冠状面)。 |
|||||||||||||||
 |
三色染色显示出亮蓝色的机化的脑脓肿壁的结缔组织。右侧是正常的脑组织,左侧是脓肿中心。 This trichrome stain demonstrates the light blue connective tissue in the wall of an organizing cerebral abscess. Normal brain is at the right and the center of the abscess at the left. |
|||||||||||||||
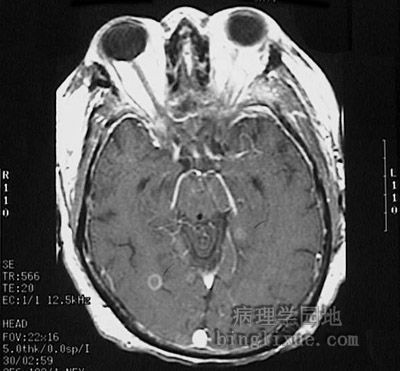 |
头颅横断面MRI显示败血症病人小的脑脓肿。 This magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the head in transverse (axial) view demonstrates a small abscess in the brain in a patient who had septicemia. |