
 |
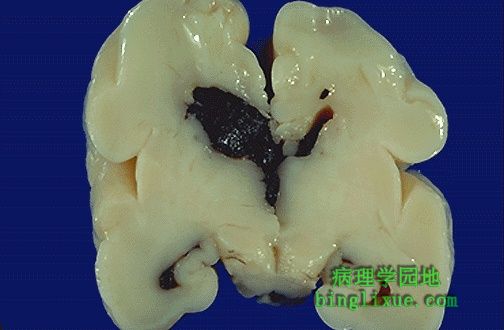
室管下区(生发基质)脑室内出血(IVH),患者为28孕周的早产儿。在发育期间,生发基质易出现这样的损害,使得IVH成为早产的并发症。 This is intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) which arose in the subependymal region (germinal matrix) of a 28 week gestational age newborn. The germinal matrix region is very susceptible to such lesions at this period of development, leading to IVH as a complication of prematurity. |
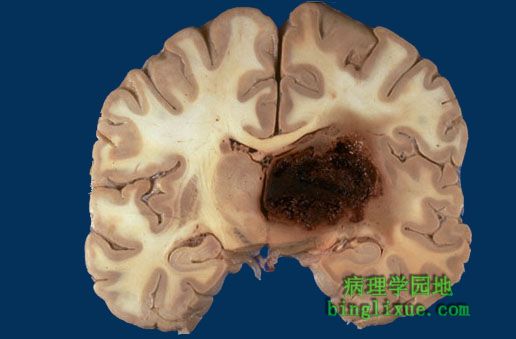 |
累及基底节的出血多为非创伤性,由高血压引起,高血压破坏和削弱小贯穿动脉,可见出血肿块使正中线移位,通常继发脑水肿,可形成脑疝。 Hemorrhages involving the basal ganglia area (the putamen in particular) tend to be non-traumatic and caused by hypertension, which damages and weakens the small penetrating arteries. A mass effect with midline shift, often with secondary edema, may lead to herniation. |
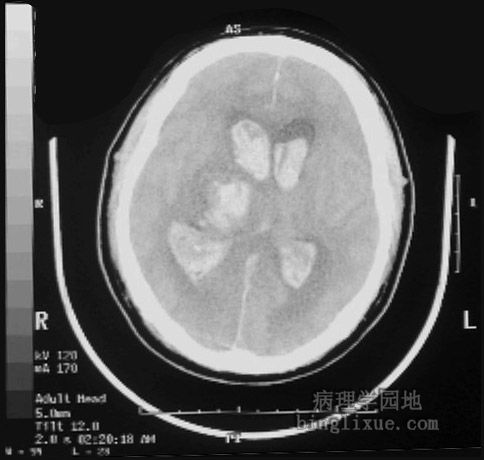 |
CT显示高血压病右侧丘脑出血,并延伸至脑室,此区出血不适于外科手术清除血肿。 This is a computed tomographic (CT) scan demonstrating a hypertensive hemorrhage in the right thalamus that has extended into the ventricular system. Hemorrhages in this location are not amenable to surgical intervention with removal of the blood. |
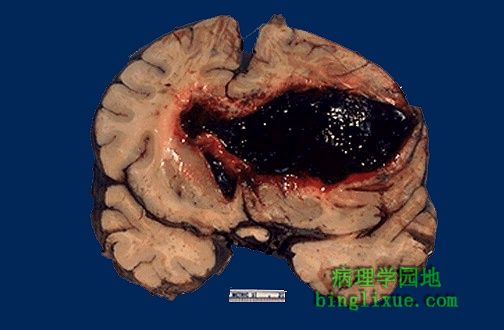 |
成年高血压病人基底节区大出血,这是引发“中风”的一个原因。 The large hemorrhage in this adult brain arose in the basal ganglia region of a patient with hypertension. This is one cause for a "stroke". |
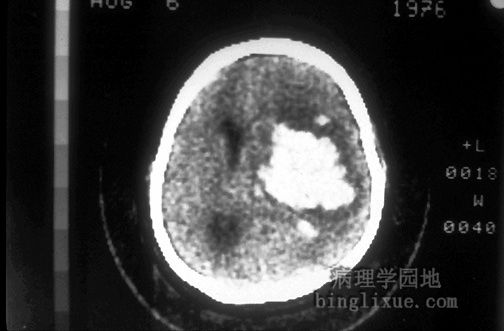 |
CT显示曾患高血压病病人颅内出血人。 This computed tomographic (CT) scan of the head in transverse view demonstrates an area of hemorrhage in a patient with a history of hypertension. |
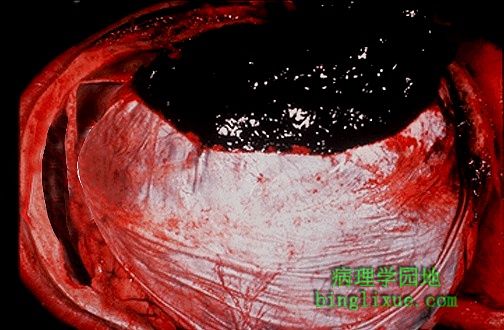 |
硬脑膜外表面可见一血块,此为硬膜外血肿。此部位的出血几乎总是脑膜中动脉撕裂造成的。 A blood clot is seen over the external surface of the dura. Thus, this is an epidural hematoma. Such a location for hemorrhage is virtually always the result of trauma that causes a tear in the middle meningeal artery. |
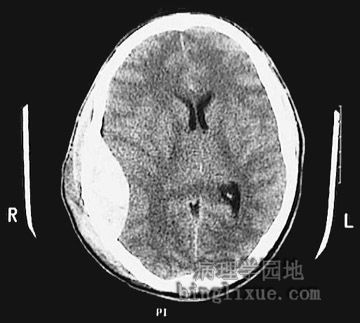 |
CT显示右侧硬膜外血肿,脑组织推向左侧,脑室变得狭小。 This is a sagittal head CT scan without contrast demonstrating a large epidural hematoma with right to left shift and ventricular narrowing. |
 |
|
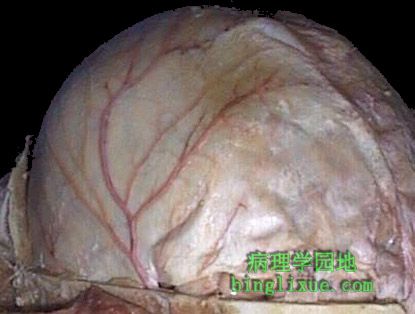 |
去除颅骨显示脑膜中动脉,其从蝶骨棘孔穿出分布于硬脑膜表面。 The top of the skull is removed to reveal the middle meningeal artery which has emerged from the foramen spinosum to branch over the surface of the dura. |
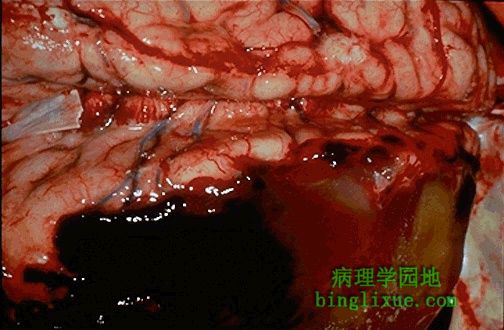 |
硬脑膜折起(右下可见小部分硬脑膜)显示硬膜下血肿。这种血块通常是桥静脉撕裂造成的。 The dura has been reflected back (with a small portion visible at the lower right) to reveal a subdural hematoma. Such a blood clot is usually the result of trauma with tearing of the bridging veins. |