
 |
对患肌萎缩侧索硬化的病人脊髓进行Luxol-fast-blue染色,显示伴有神经胶质增生的脊髓侧索变性--ALS硬化。 This Luxol-fast-blue stain of spinal cord in a patient with ALS demonstrates lateral column degeneration with gliosis--the "sclerosis" of ALS. |
 |
Tay-Sachs病的婴儿会出现扩大的苍白色神经元,这在欧洲犹太后裔最常见。通常疾病最先在 6 个月时被发现,因为此时婴儿不能继续发育。 These enlarged, pale neurons are in a baby with Tay-Sachs disease, which is seen mostly in persons of European Jewish heritage. The disease is often first noticed at an age of 6 months, because the baby is not progressing developmentally. |
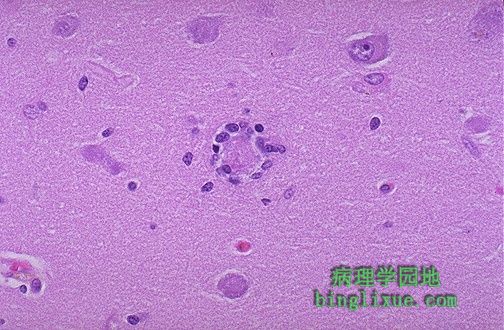 |
噬神经细胞现象,这个垂死的神经元被周围小胶质细胞包围。 This is an example of neuronophagia in which a dying neuron is surrounded by microglial cells. |
 |
大脑皮质处所谓的假层式坏死,这是持久性植物神经状态的典型表现,病人需要生命维持系统才能存活。注意由于皮质丧失,皮质边缘变得很薄。 This is a so-called pseudolaminar necrosis of the cerebral cortex that is typical of a patient in a persistent vegetative state who is on life-support systems. Note that the cortical ribbon is very thin because of the loss of cortex. |
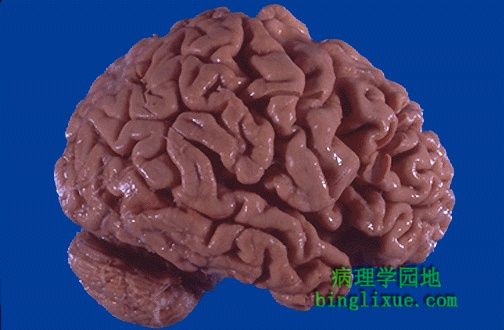 |
图示脑萎缩主要发生在额叶和顶骨区域,表现为典型的脑回变窄和脑沟变宽。这里萎缩归因于Alzheimer老年痴呆(Alzheimer病)。 The cerebral atrophy seen here mainly in the frontal and parietal regions is characterized by narrowed gyri and widened sulci. The atrophy seen here was due to senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type (Alzheimer's disease). |
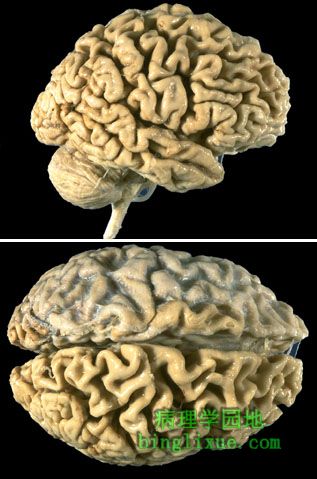 |
Alzheimer病例,两图可见很多明显的萎缩,并累及枕骨区域。 In this case of Alzheimer's disease, there is more marked atrophy seen superiorly and laterally, with sparing of the occipital region. |
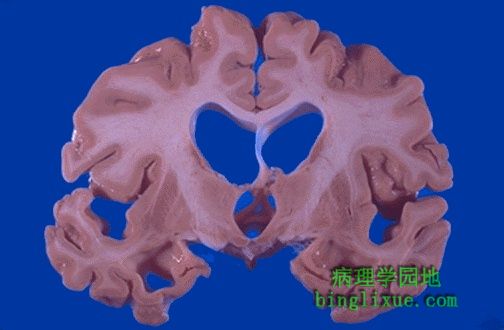 |
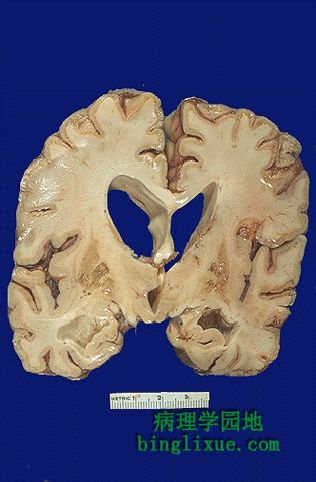
皮质萎缩导致脑室代偿性扩大,诸如众所周知的脑积水。 The cortical atrophy leads to compensatory dilation of the cerebral ventricles known as "hydrocephalus ex vacuo". |
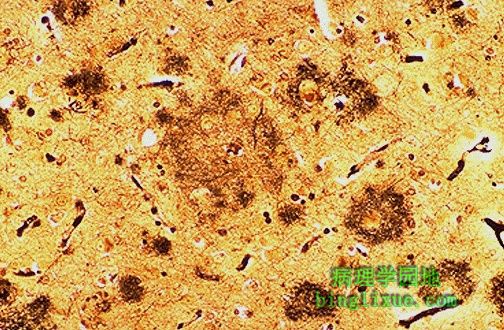 |
Alzheimer病典型的显微镜表现包括“老年斑”与星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞,老年斑是变性的突触前末梢。采用银染色很容易看到这些斑块,如图所示,许多斑块的大小各异。 The characteristic microscopic findings of Alzheimer's disease include "senile plaques" which are collections of degenerative presynaptic endings along with astrocytes and microglia. These plaques are best seen with a silver stain, as seen here in a case with many plaques of varying size. |
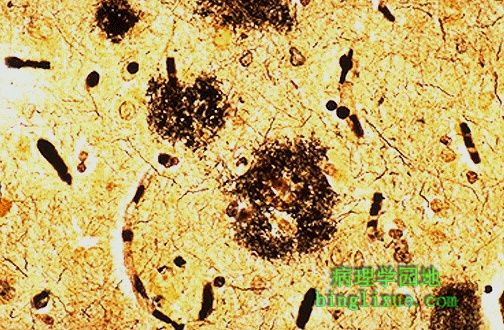 |
银染色Alzheimer 病显示老年斑,多位于大脑皮质和海马。痴呆的主要表现是进行性记忆丧失。 The plaques of Alzheimer's disease are seen here with a silver stain. Such plaques are most numerous in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. This dementia is marked mainly by progressive memory loss. |
 |
Alzheimer病引起的很多神经炎斑块。刚果红染色显示淀粉样核心。一些外周脑动脉也可能受累及。还可能出现与β淀粉样蛋白相关的问题,但具体的发病机制不是很清楚。有趣的是,淀粉样蛋白遗传密码位于21号染色体上,并且活到40岁的21三体症患者出现Alzheimer病不尽相同。 A number of neuritic plaques with Alzheimer's disease are seen here. They have an amyloid core as seen here with Congo red stain. Small peripheral cerebral arteries may also be involved. There appears to be a problem with beta amyloid precursor protein, but the exact pathogenesis is unknown. It is interesting that the gene coding for cerebral amyloid is on chromosome 21--and persons with trisomy 21 living to age 40 invariably develop Alzheimer's disease. |