
 |
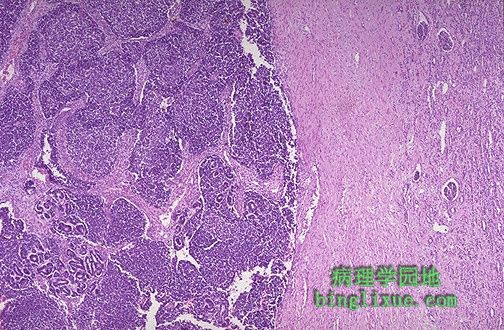
wilms瘤镜下见主要是由巢状和片状的暗蓝色细胞构成,位于左侧压迫右侧的正常肾实质。) This is a Wilm's tumor that is composed microscopically of nests and sheets of dark blue cells at the left with compressed normal renal parenchyma at the right. |
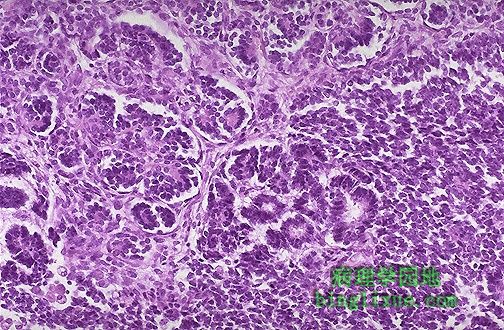 |
高倍镜wilms瘤类似于起源组织胚胎期结构。肿瘤倾向于形成幼稚的肾小球和肾小管样结构。 Wilm's tumor resembles the fetal nephrogenic zone of the kidney. The tumor shows attempts to form primitive glomerular and tubular structures. |
 |
正常肾小球,肾小球血管袢薄而清晰。内皮细胞和系膜细胞数目正常。周围的肾小管也正常。健康状态良好。 This is a normal glomerulus by light microscopy. The glomerular capillary loops are thin and delicate. Endothelial and mesangial cells are normal in number. The surrounding tubules are normal. Life is good. |
 |
正常肾小球,PAS染色以突出基底膜。肾小球血管袢薄而清晰。 This normal glomerulus is stained with PAS to highlight basement membranes. The capillary loops of the glomerulus are well-defined and thin. |
 |
图示正常肾小球。注意血管袢和系膜的关系。15%的肾小球滤过通过系膜,其它的通过有孔的血管内皮细胞滤过。正常的阴离子屏障阻止象白蛋白这样的蛋白分子从内膜通过。正常系膜含2~4个具有巨噬细胞的功能的系膜细胞。 A normal glomerulus is shown diagramatically. Note the relationship of the capillary loops to the mesangium. About 15% of glomerular filtration occurs through the mesangium, with the remainder through the fenestrated epithelium. The normal anionic charge barrier prevents protein molecules such as albumin from passing through the endothelium. The normal mesangium contains about 2 to 4 mesangial cells, which have a macrophage-like function. |
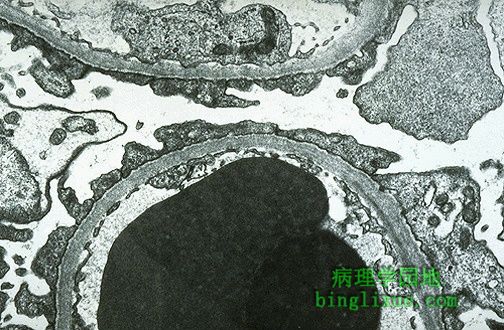 |
微小病变性肾小球肾炎,特点是:脏层上皮细胞(足细胞)的足突消失,正常的离子屏障丧失,表现为选择性白蛋白漏出,接着出现蛋白尿。光镜下,微小病变的肾小球是正常的。在这张电镜照片的下半部的毛细血管袢中有2个高电子密度的RBC。可见有窗孔的内皮细胞及正常的基底膜。然而,脏层上皮细胞(足细胞)表面的足突消失或融合。 This is minimal change disease (MCD) which is characterized by effacement of the epithelial cell (podocyte) foot processes and loss of the normal charge barrier such that albumin selectively leaks out and proteinuria ensues. By light microscopy, the glomerulus is normal with MCD. In this electron micrograph, the capillary loop in the lower half contains two electron dense RBC's. Fenestrated endothelium is present, and the basement membrane is normal. However, overlying epithelial cell foot processes are effaced (giving the appearance of fusion) and run together. |
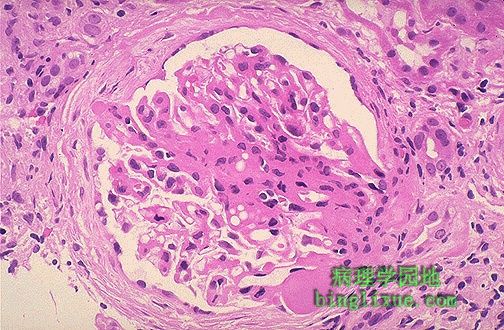 |
局灶性节段性肾小球硬化,肾小球中央有一片胶原硬化区。和微小病变性肾炎相比,局灶性节段性肾小球硬化的病人更容易发生非选择性蛋白尿、血尿、可发展为慢性肾衰、对皮质类固醇治疗不敏感。 This is focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). An area of collagenous sclerosis runs across the middle of this glomerulus. In contrast to minimal change disease, patients with FSGS are more likely to have non-selective proteinuria, hematuria, progression to chronic renal failure, and poor response to corticosteroid therapy. |
 |
局灶性节段性肾小球硬化,三色染色显示蓝色的胶原沉积。成年人和儿童肾病综合征有1/6是局灶性节段性肾小球硬化。 This trichrome stain of a glomerulus in a patient with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) demonstrates blue collagen deposition. FSGS accounts for about a sixth of cases of nephrotic syndrome in adults and children. |
 |
肾小球充满细胞,毛细血管袢分辨不清,为增生性肾小球肾炎,也称作链球菌感染后肾小球肾炎。 This glomerulus is hypercellular and capillary loops are poorly defined. This is a type of proliferative glomerulonephritis known as post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. |
 |
链球菌感染后的细胞大量增生,表现为在毛细血管袢内及周围的血管内皮细胞、系膜细胞增生,伴中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞浸润。可在A组β溶血性链球菌感染数周后发生。病人抗O(ASO)滴度明显升高。 The hypercellularity of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis is due to increased numbers of epithelial, endothelial, and mesangial cells as well as neutrophils in and around the capillary loops. This disease may follow several weeks after infection with certain strains of group A beta hemolytic streptococci. Patients typically have an elevated anti-streptolysin O (ASO) titer. |