
 |
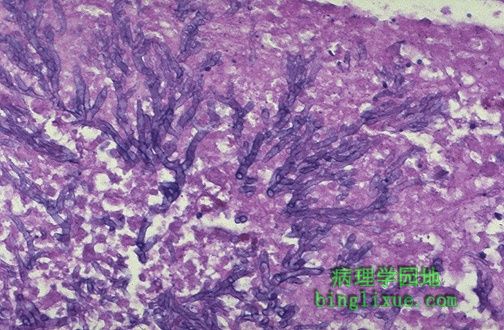
高倍镜下曲霉菌菌丝清楚可见。曲霉菌有浸润血管的倾向。 The hyphae of Aspergillus are seen more clearly here. Aspergillus has a propensity to invade into blood vessels. |
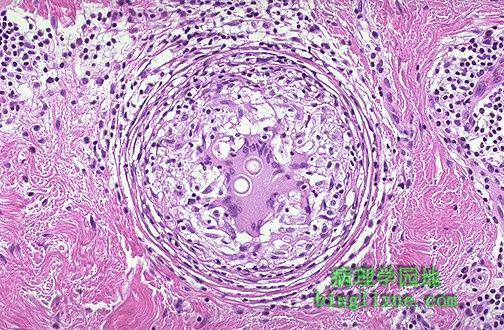 |
典型的肉芽肿中央有一大的朗格罕斯巨细胞。巨细胞内可见到两个粗球孢子菌小球。 This well-formed granuloma has a large Langhans giant cell in the center. Two small spherules of Coccidioides immitis are seen in the giant cell. |
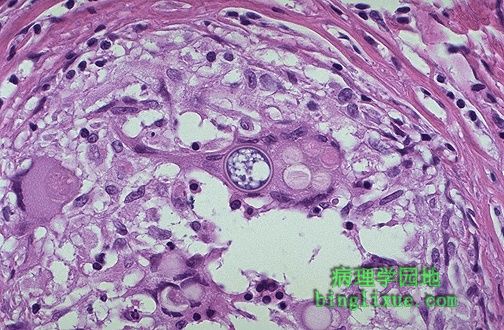 |
高倍镜下可见巨细胞内的孢子菌(C. immitis)小球体厚壁。小球体包含内生孢子。在美国,孢子菌(C. immitis)仅出现在西南部。 At higher magnification, the thick wall of the C. immitis spherule is seen in a giant cell in the center of the photomicrograph. The spherule contains endospores. In the United States, C. immitis is endemic to the southwest. |
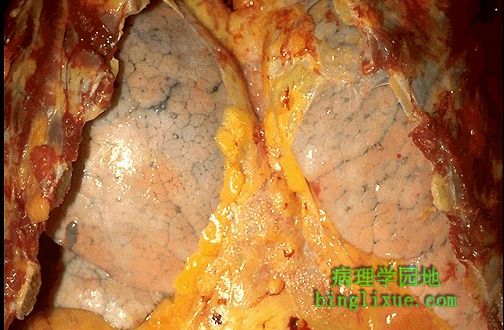 |
肺外观基本上正常,但呈现过度充气状态,病人死于哮喘持续状态。 These lungs appear essentially normal, but are normal-appearing because they are the hyperinflated lungs of a patient who died with status asthmaticus. |
 |
死于哮喘持续状态病人的肺切面基本正常。 The cut section of the hyperinflated lung of a patient dying in status asthmaticus appears essentially normal. |
 |
通过粘液和模仿咳嗽建立哮喘发作时病人的支气管树模型。粘液由支气管粘膜下腺的肥大细胞分泌,支气管收缩,以及粘液脱水浓缩来形成粘液栓,阻塞哮喘病人气道。 This cast of the bronchial tree is formed of inspissated mucus and was coughed up by a patient during an asthmatic attack. The outpouring of mucus from hypertrophied bronchial submucosal glands, the bronchoconstriction, and dehydration all contribute to the formation of mucus plugs that can block airways in asthmatic patients. |
 |
在右侧的支气管软骨和左侧充满粘液的支气管腔之间,平滑肌增生,水肿,炎症(主要是嗜酸性粒细胞)等因素使粘膜下层增厚。这些是支气管哮喘的病变。哮喘发作时外周嗜酸细胞计数或痰嗜酸细胞计数增加。 Between the bronchial cartilage at the right and the bronchial lumen filled with mucus at the left is a submucosa widened by smooth muscle hypertrophy, edema, and inflammation (mainly eosinophils). These are changes of bronchial asthma. The peripheral eosinophil count or the sputum eosinophils can be increased during an asthmatic attack. |
 |
高倍镜下支气管哮喘可见大量嗜酸性细胞,可见明显的粉红色嗜酸性颗粒。哮喘有2种临床类型,它们彼此相关。 At high magnification, the numerous eosinophils are prominent from their bright red cytoplasmic granules in this case of bronchial asthma. There are two major clinical forms of asthma that can overlap.
|
 |
阻塞性肺病支气管扩张症。当出现阻塞和炎症感染时,引起永久性支气管扩张。一旦出现扩张的支气管,就如图肺中下部所见。反复感染、咳大量脓痰是其特征。 This is another form of obstructive lung disease known as bronchiectasis. Bronchiectasis occurs when there is obstruction or infection with inflammation and destruction of bronchi so that there is permanent dilation.Once the dilated bronchi are present, as seen here grossly in the mid lower portion of the lung, the patient has recurrent infections because of the stasis in these airways. Copius purulent sputum production with cough is typical. |
 |
支气管扩张症显示扩张支气管病灶。在出现如肿瘤、吸入性异物等病变过程时,堵塞部分气道,支气管扩张就容易在局部发生。广泛的支气管扩张对囊性纤维化的病人来说很典型,病人反复感染,粘液阻塞遍及全肺。 A closer view demonstrates the focal area of dilated bronchi with bronchiectasis. Bronchiectasis tends to be localized with disease processes such as neoplasms and aspirated foreign bodies that block a portion of the airways. Widespread bronchiectasis is typical for patients with cystic fibrosis who have recurrent infections and obstruction of airways by mucus throughout the lungs. |