
 |
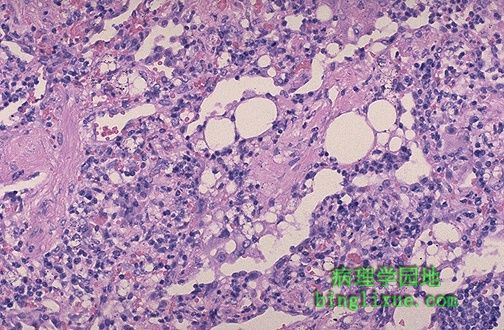
外源性类脂性肺炎,沿气道处可见脂泡,并伴异物巨细胞炎症反应。外源性是指脂质源于体外,而后被吸入到支气管树。 This is the microscopic appearance of an exogenous lipid pneumonia in which lipid vacuoles appear, mainly along airways, accompanied by an inflammatory response that can contain foreign body giant cells. The term exogenous refers to the origin of the lipid material outside the body. This material is aspirated into the bronchial tree. |
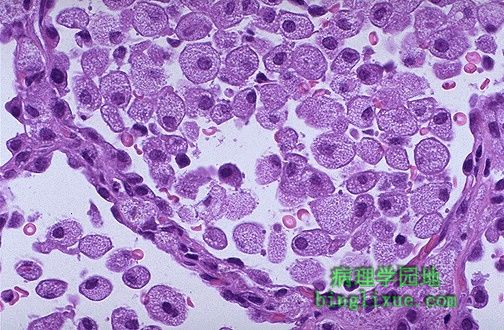 |
内源性类脂性肺炎,肺泡中可见大量泡沫状充满脂质的巨噬细胞。内源性是指肺和血管破裂释放脂质,通常出现在栓塞的远端(如肿瘤,吸入性异物,或支气管扩张症)。巨噬细胞聚集起来吞噬脂质。 This is the microscopic appearance of an endogenous lipid pneumonia in which numerous foamy lipid laden macrophages are present in alveolar spaces. The term endogenous refers to the origin of the lipid material from breakdown of lung and blood, usually distal to the site of an obstructive process (such as a neoplasm, an inhaled foreign body, or bronchiectasis). The macrophages collect to ingest the lipid material. |
 |
肺结核可见散在淡黄*色肉芽肿,主要出现在肺上部。一些较大的肉芽肿中央有干酪样坏死。肺肉芽肿疾病大致表现为大小不一的圆形结节,质地坚韧,呈淡黄*色。较大的结节可能存在中央部位的干酪样坏死--包括液化性坏死和凝固性坏死的过程)。 Here is the gross appearance of a lung with tuberculosis. Scattered tan granulomas are present, mostly in the upper lung fields. Some of the larger granulomas have central caseation. Granulomatous disease of the lung grossly appears as irregularly sized rounded nodules that are firm and tan. Larger nodules may have central necrosis known as caseation--a process of necrosis that includes elements of both liquefactive and coagulative necrosis). |
 |
另例肺肉芽肿性疾病。小结节经常向肺上叶发展说明肉芽肿过程,而不是肿瘤转移。 This is another example of granulomatous disease of the lung. The pattern of smaller nodules which have a propensity for upper lobe involvement suggests a granulomatous process rather than metastatic disease. |
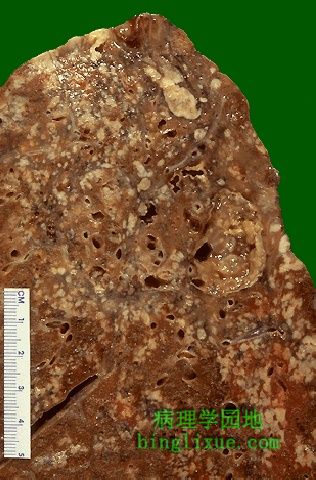 |
肉芽肿干酪性坏死。图示广泛肉芽肿病变。原发于肺尖部的多个干酪样肉芽肿是继发性肺结核的最典型特征。然而真菌性肉芽肿(组织胞浆菌病,隐球菌病,球孢子菌病)也具有这样的外观。 On closer inspection, the granulomas have areas of caseous necrosis. This is very extensive granulomatous disease. This pattern of multiple caseating granulomas primarily in the upper lobes is most characteristic of secondary (reactivation) tuberculosis. However, fungal granulomas (histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, coccidioidomycosis) can mimic this pattern as well. |
 |
当存在广泛的干酪性坏死并且肉芽肿累及较大的支气管时,大量的坏死物排出,留下空洞。对于伴有大肉芽肿的肺结核而言,空洞非常典型,常发生于肺上叶。 When there is extensive caseation and the granulomas involve a larger bronchus, it is possible for much of the soft, necrotic center to drain out and leave behind a cavity. Cavitation is typical for large granulomas with tuberculosis. Cavitation is more common in the upper lobes. |
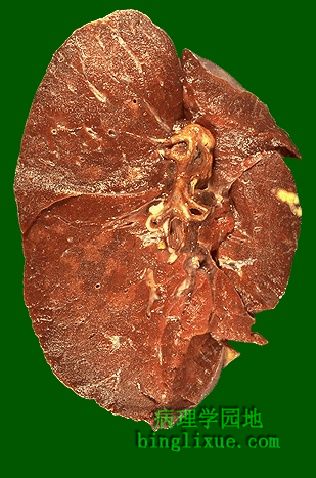 |
右边肺中间区域有一个小块黄褐色的胸膜下肉芽肿。在肺门淋巴结靠近支气管处有一个小块黄褐色肉芽肿。称为高恩综合症(原发综合征),它是原发性肺结核的典型表现。多数人,肉芽肿疾病不会继续进展,会逐渐变小并钙化。胸片显示一局部钙化灶,说明病人以前患过肉芽肿疾病。 There is a small tan-yellow subpleural granuloma in the mid-lung field on the right. In the hilum is a small yellow tan granuloma in a hilar lymph node next to a bronchus. This is the "Ghon complex" that is the characteristic gross appearance with primary tuberculosis. In most persons, the granulomatous disease will not progress. Over time, the granulomas decrease in size and can calcify, leaving a focal calcified spot on a chest radiograph that suggests remote granulomatous disease. |
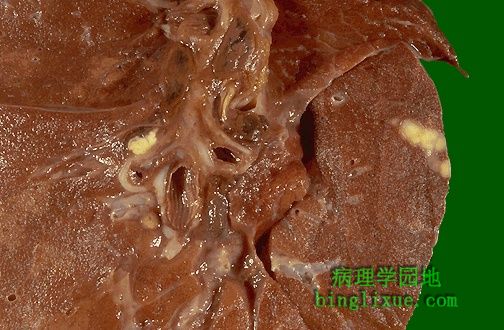 |
高恩综合症(原发综合征),原发性肺结核外观,发生于儿童,结核菌初次感染。继发性肺结核主要见于成年人。 The Ghon complex is seen here at closer range. Primary tuberculosis is the pattern seen with initial infection with tuberculosis in children. Reactivation, or secondary tuberculosis, is more typically seen in adults. |
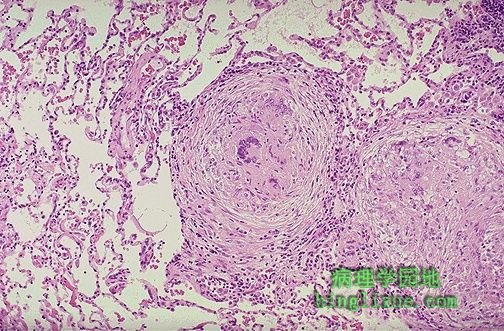 |
边界清楚的肉芽肿,圆形。图片中心的一个肉芽肿包含几个朗格罕斯巨细胞。肉芽肿由巨噬细胞而来的上皮样细胞,以及少量淋巴细胞,中性粒细胞,浆细胞,成纤维细胞组成。局部化的较小的肉芽肿提示免疫反应相当强。 Well-defined granulomas are seen here. They have rounded outlines. The one toward the center of the photograph contains several Langhans giant cells. Granulomas are composed of transformed macrophages called epithelioid cells along with lymphocytes, occasional PMN's, plasma cells, and fibroblasts. The localized, small appearance of these granulomas suggests that the immune response is fairly good. |
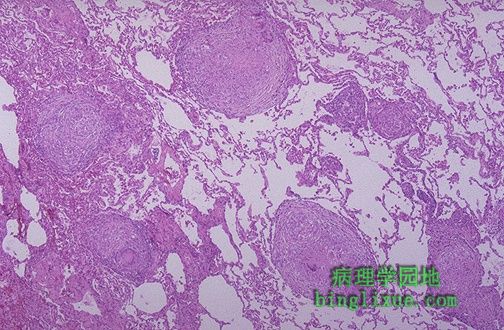 |
低倍镜显示了多个肉芽肿。肉芽肿疾病胸片显示网点状致密阴影。 At low magnification, this photomicrograph reveals multiple granulomas. Granulomatous disease by chest radiograph can appear as reticulonodular densities. |