
 |
沿着降结肠有几个憩室。肠壁的薄弱部位和腔内压力增加,促进了肠憩室的形成。 Several diverticula are seen along the length of the descending colon. Focal weaknesses in the bowel wall and increased lumenal pressure contribute to the formation of diverticula. |
 |
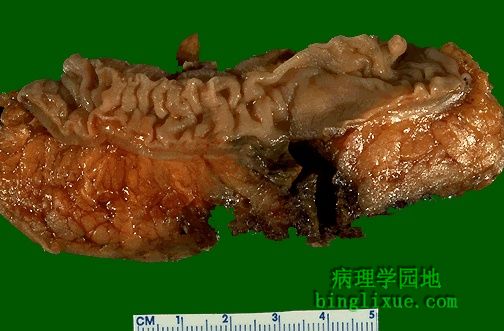
已打开的结肠显示非炎症性憩室。每个憩室有一个窄的开口通向结肠腔。 The colon has been opened to reveal the presence of non-inflamed diverticula. Each has an opening to the colonic lumen through a narrow neck. |
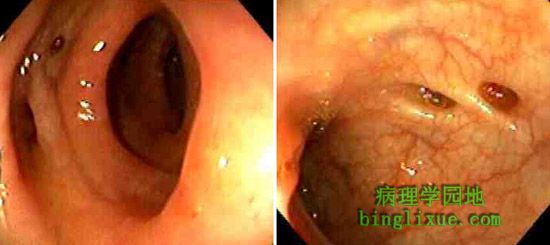 |
憩室的结肠镜检图。 Colonoscopic views of diverticula are seen here. |
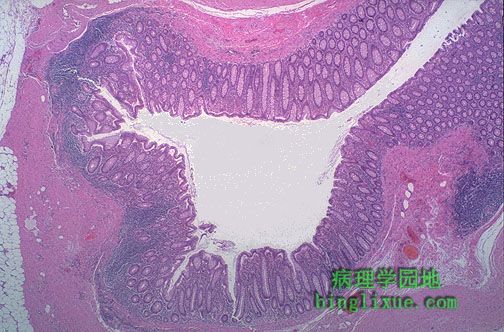 |
低倍镜下,结肠憩室有内覆粘膜的中心腔,然而腔壁(因缺少肌层)是薄弱。憩室的窄颈可能会被侵蚀破坏。 At low magnification, a colonic diverticulum has a central lumen with surrounding mucosa, while the wall (lacking a muscularis) is attenuated. The narrow neck of the diverticulum may become eroded. |
 |
憩室炎结肠表面充血。大便刺激憩室肠侵蚀的粘膜产生炎症和出血。 The surface of the colon is hyperemic because of inflammation as a result of diverticulitis. The erosion of the mucosa by the stool in the diverticula can produce inflammation and hemorrhage. |
 |
憩室炎并破裂,见黑褐色的不规则的管道从黏膜表面向下延伸。 This diverticulum has become inflamed and has ruptured outward, seen as the dark brown irregular tract extending down from the mucosal surface here. |
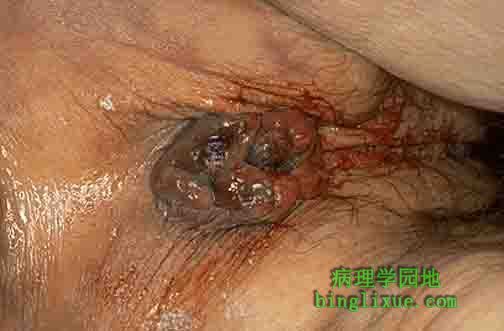 |
可见肛门和肛周有明显的真性痔脱垂(内痔)。痔疮由扩张的黏膜下血管形成,此黏膜下血管可形成血栓和破损伴有血肿的形成。外痔形成超过内括约肌,在肛门边缘产生一个“急性隆起”。慢性便秘、慢性腹泻、怀孕和门静脉高压均能刺激痔形成。痔疮发痒、出血(在损伤过程中通常是鲜红的血)。 Seen here is the anus and perianal region with prominent prolapsed true (internal) hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids consist of dilated submucosal veins which may thrombose and rupture with hematoma formation. External hemorrhoids form beyond the intersphincteric groove to produce an "acute pile" at the anal verge. Chronic constipation, chronic diarrhea, pregnancy, and portal hypertension enhance hemorrhoid formation. Hemorrhoids can itch and bleed (usually bright red blood, during defacation). |
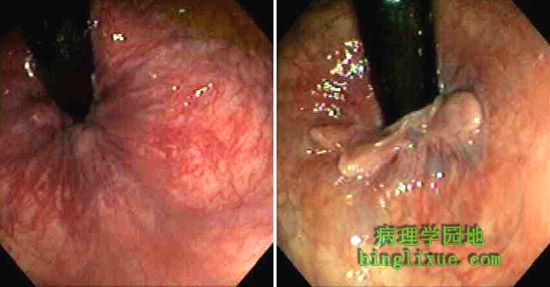 |
肛门直肠交界处的痔疮的结肠镜检图。 Seen here is on colonoscopy are views of hemorrhoids at the anorectal junction. |
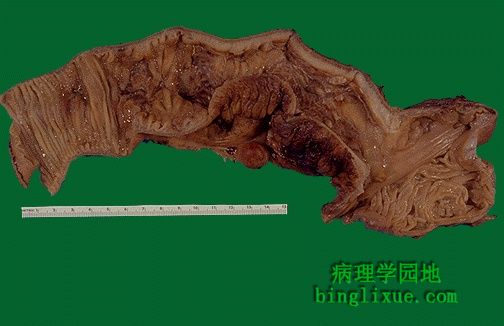 |
回肠末段Crohn病。虽然胃肠道的任何部位都可患Crohn病,但空肠和回肠末段尤易发。可见肠中部肠壁增厚、黏膜已经失去了规则的粘膜皱襞。浆膜表面有略带红色坚硬的脂肪组织已蔓延至其表面。浆膜的炎症导致了粘连。炎症病变呈阶段性不连续。 This portion of terminal ileum demonstrates the gross findings with Crohn's disease. Though any portion of the gastrointestinal tract may be involved with Crohn's disease, the small intestine--and the terminal ileum in particular--is most likely to be involved. The middle portion of bowel seen here has a thickened wall and the mucosa has lost the regular folds. The serosal surface demonstrates reddish indurated adipose tissue that creeps over the surface. Serosal inflammation leads to adhesions. The areas of inflammation tend to be discontinuous throughout the bowel. |
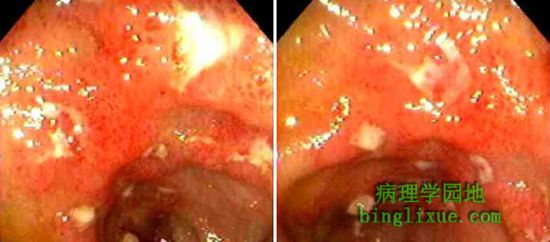 |
结肠镜检查的内窥镜表现为黏膜红斑和破损。 The endoscopic appearance with colonoscopy, demonstrating mucosal erythema and erosion, is seen here |