
 |
低倍镜显示多发性骨髓瘤异常浆细胞弥漫浸润骨髓。 At low power, the abnormal plasma cells of multiple myeloma fill the marrow. |
 |
中倍镜显示多发性骨髓瘤的浆细胞与正常浆细胞很相似,但分化较差。通常浆细胞分化成熟,具有产生免疫球蛋白的功能。然而骨髓瘤可通过蛋白电泳中免疫球蛋白的“波峰”或者在尿液中的Bence-Jones蛋白(轻链)的存在而被检测出来。免疫电泳能有效区分产生的单克隆免疫球蛋白的类型。 At medium power, the plasma cells of multiple myeloma here are very similar to normal plasma cells, but they may also be poorly differentiated. Usually, the plasma cells are differentiated enough to retain the function of immunoglobulin production. Thus, myelomas can be detected by an immunoglobulin "spike" on protein electrophoresis, or the presence of Bence-Jones proteins (light chains) in the urine. Immunoelectrophroesis characterizes the type of monoclonal immunoglobulin being produced. |
 |
多发性骨髓瘤骨髓涂片可见很多浆细胞,核偏位,核周围胞浆透亮清晰。 Here is a smear of bone marrow aspirate from a patient with multiple myeloma. Note that there are numerous plasma cells with eccentric nuclei and a perinuclear halo of clearer cytoplasm. |
 |
图示5厘米的淋巴结(淋巴结病)。正常的淋巴结应该是质软、粉红色、直径小于1厘米。这个淋巴结与霍奇金淋巴瘤有关。肉眼外观与非霍奇金淋巴瘤的类似。 Here is a 5 cm lymph node (obviously from a patient with lymphadenopathy). The node should normally be soft and pink and less than 1 cm in size. This lymph node is involved with Hodgkin's disease. This gross appearance could pass for a non-Hodgkin's lymphoma as well. |
 |
霍奇金淋巴瘤病人肝脏。霍奇金淋巴瘤分期决定治疗,因而判断病人是否为只有单一淋巴结区域受累还是多淋巴结区域受累或有结外器官受累就显得非常重要。图示的肝脏与非霍奇金淋巴瘤肝脏病变相似。 This is a liver that is involved with Hodgkin's disease. The staging of Hodgkin's disease is very important in determining therapy. Thus, it is important to determine whether the patient has only a single lymph node region involved, multiple node regions, or extranodal involvement. This picture could probably suffice for non-Hodgkin's lymphomatous hepatic disease as well. |
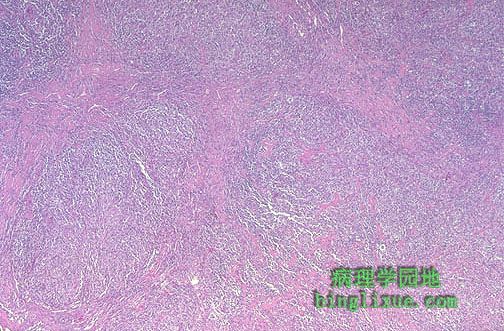 |
结节硬化型霍奇金淋巴瘤。图示粉红色的胶原束伸入并分隔淋巴组织。 This is Hodgkin's disease, nodular sclerosis type. Note the bands of pink collagenous tissue dividing the field in this lymph node. |
 |
中倍镜下结节硬化型霍奇金淋巴瘤有明显的纤维束。霍奇金淋巴瘤的分期对治疗和预后都很重要 。分期常常是通过放射手段完成的,CT扫描用来定位病变淋巴结,超声和胸片用来判断淋巴结的大小和肝、脾病变。对受累淋巴结进行活检是非常重要的,骨髓活检也是如此。因X线的广泛应用,剖腹探察现在已很少用。 At medium power, nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease has prominent bands of fibrosis. Staging of Hodgkin's disease is important to try and determine therapy and the prognosis. Staging is often done by radiographic means, with CT scans used to determine where lymphadenopathy is located, ultrasonography to determine size and lesions of liver and spleen, and chest radiograph. Histologic diagnosis is typically made from biopsy of an involved lymph node. A bone marrow biopsy is typically performed as well. Staging laparotomy is less commonly used nowadays because the radiographic procedures are excellent. |
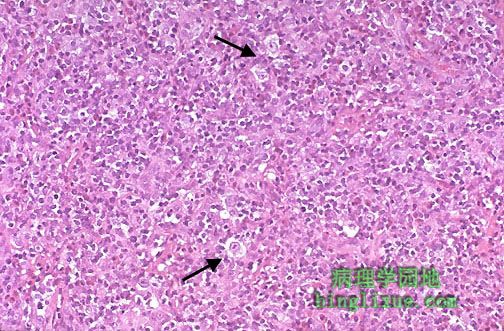 |
高倍镜下见福尔马林固定后的细胞,可见散在的大细胞(陷窝细胞),边界清晰,位于陷窝中(因福尔马林固定时胞质收缩,细胞似位于陷窝中),是结节硬化型霍奇金淋巴瘤的典型表现。 At high power, there are scattered large cells with a surrounding prominent clear space, an artefact of formalin fixation. These are the lacunar cells characteristic for the nodular sclerosis type of Hodgkin's disease. |
 |
箭头所示RS细胞,细胞体积大,核仁明显,是霍奇金淋巴瘤特征性Reed-Sternberg细胞。霍奇金淋巴瘤病灶内见大量反应性淋巴细胞。霍奇金淋巴瘤主要有四种亚型:淋巴细胞为主型,结节硬化型,混合细胞型,和淋巴细胞消减型。 Note the large cells with large, pale nuclei containing large purple nucleoli at the arrowheads. These are Reed-Sternberg cells that are indicative of Hodgkin's disease. Most of the cellular content of foci of Hodgkin's disease consists of reactive lymphoid cells. There are four main subtypes of Hodgkin's disease: lymphocyte predominance, nodular sclerosis, mixed cellularity, and lymphocyte depletion. |
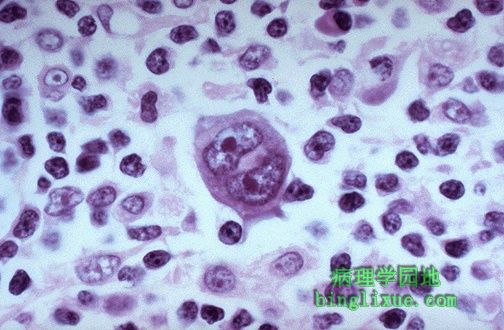 |
霍奇金淋巴瘤,Reed-Sternberg 细胞可见大而明显的核仁。 This is a high power view of a Reed-Sternberg cell seen with Hodgkin's disease. Note the large, prominent nucleoli. |