
 |
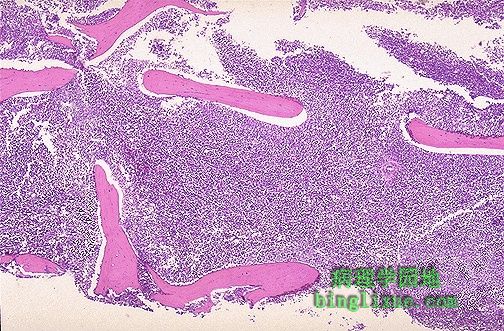
典型的白血病有很多不正常的细胞充满骨髓,取代正常的造血功能。这里的骨髓基本上100%是细胞,基本上是由白血病细胞组成的。由于取代正常组织或抑制干细胞的分裂,使得正常的造血功能降低。因此,白血病病人有贫血、血小板减少、粒细胞减少和所有继发并发症的倾向,明显的并发症是出血和感染。 Leukemias typically fill up the marrow with abnormal cells, displacing normal hematopoiesis. The marrow here is essentially 100% cellular, but composed almost exclusively of leukemic cells. Normal hematopoiesis is reduced via replacement (a "myelophthisic" process) or by suppressed stem cell division. Thus, leukemic patients are prone to anemia, thrombocytopenia, and granulocytopenia and all of the complications that ensue, particularly complications of bleeding and infection. |
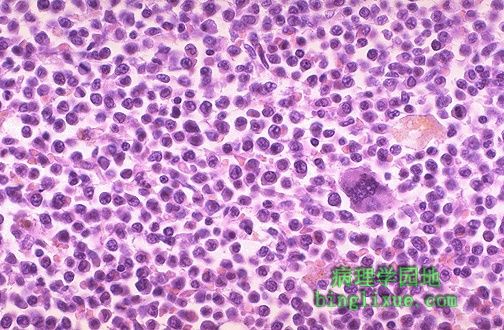 |
在高倍镜下,见到的是急性髓母细胞白血病骨髓。在右侧中心处有一个孤立巨核细胞。 At high power, the bone marrow of a patient with acute myelogenous leukemia is seen here. There is one lone megakaryocyte at the right center. |
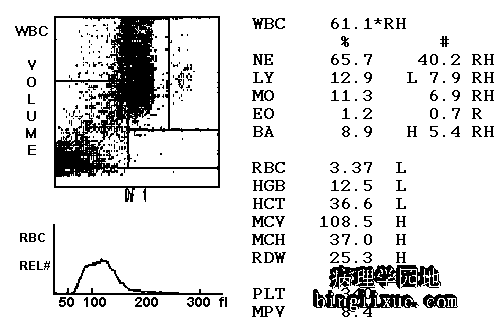 |
全血细胞计数显示慢性粒细胞白血病病人有明显的白细胞计数增加。 The CBC here is from a patient with CML. Note the markedly increased WBC count. |
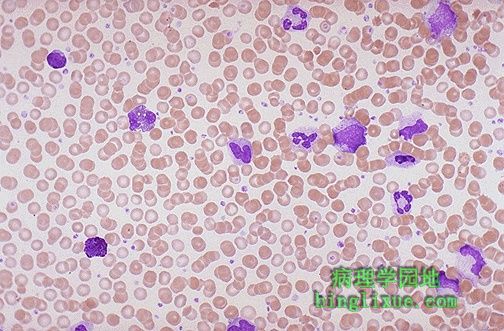 |
可见多种粒细胞形式,包括不成熟的髓细胞和杆状核嗜中性粒细胞,是一种骨髓及外骨髓增殖的状态,称为慢性髓性白血病,这种疾病在中年人常见。须与类白血病相鉴别,可用的检测是粒细胞碱性磷酸酶(LAP),慢性髓性白血病较低而类白血病反应较高。 There are numerous granulocytic forms seen here, including immature myeloid cells and bands. This condition is one of the myeloproliferative states and is known as chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) that is most prevalent in middle-aged adults. A useful test to help distinguish this disease is the leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) score, which should be low with CML and high with a leukemoid reaction. |
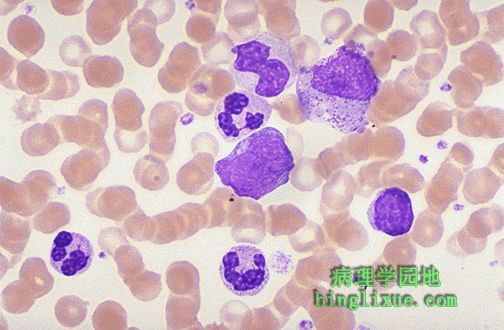 |
慢性髓性白血病外周血涂片,常见较多嗜碱性粒细胞和嗜酸性粒细胞,也有较多的杆状核嗜中性粒细胞和不成熟的髓细胞(晚幼粒和中幼粒细胞)。与急性髓母细胞白血病相比慢性髓性白血病没有更多的不成熟细胞。 Here is another view of a peripheral blood smear in a patient with CML. Often, the numbers of basophils and eosinophils, as well as bands and more immature myeloid cells (metamyelocytes and myelocytes) are increased. Unlike AML, there are not many blasts with CML. |
 |
慢性髓性白血病的髓细胞在染色体组型上有典型的费城染色体,22号染色体的q臂的一部分与9号染色体q臂的一部分易位,定义为t(9:22)。 Myeloid cells of CML are also characterized by the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph1) on karyotyping. This is a translocation of a portion of the q arm of chromosome 22 to the q arm of chromosome 9, designated t(9:22). |
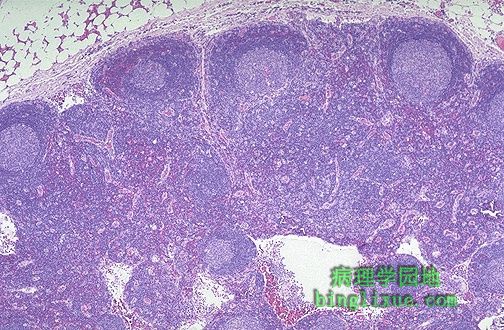 |
良性反应淋巴结的正常外观。上部是被膜,其下为被膜下淋巴窦,是淋巴的入口,排出周围组织的淋巴到淋巴结。被膜下方是有淋巴滤泡的副皮质区,淋巴滤泡有一苍白色的生发中心。下面是窦状小管延伸到淋巴结的中心。 Here is the normal appearance of a benign reactive lymph node. At the top is the capsule and just under that a subcapsular sinus where lymphatics enter that drain tissues peripheral to the node. Beneath the capsule is the paracortical zone with lymphoid follicles having a pale germinal center in which the immune responses are often generated. Beneath this are sinusoids extending to the center of the node. |
 |
在高倍镜下可见淋巴滤泡的生发中心有大的活化的淋巴细胞。右下部是被膜下淋巴窦。 At high magnification is seen a lymph node follicle with a germinal center containing larger lymphocytes undergoing activation. At the lower right is the subcapsular sinus. |
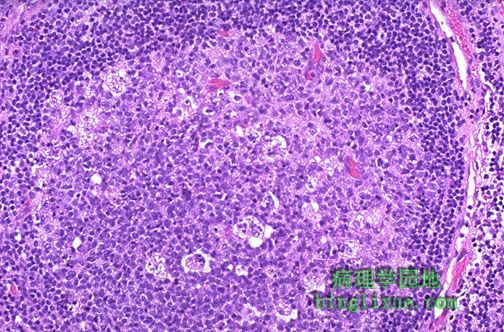 |
更明显的淋巴结的反应性改变,有较大的淋巴滤泡和包含巨噬细胞的生发中心。通常,良性反应过程的淋巴结是很可能迅速变大变软。 This is a more pronounced reactive change in a lymph node, with a larger follicle and germinal center containing macrophages. In general, lymph nodes in a benign reactive process are more likely to enlarge quickly and be tender. |
 |
高倍镜下反应性淋巴结滤泡的生发中心有明显的含不规则细胞碎片的巨噬细胞(称为“易染体巨噬细胞”)。血管也是非常明显的。 At high magnification, the germinal center in this reactive lymph node follicle has prominent macrophages with irregular cellular debris (so-called "tingible body macrophages"). Blood vessels are also more prominent. |