
 |
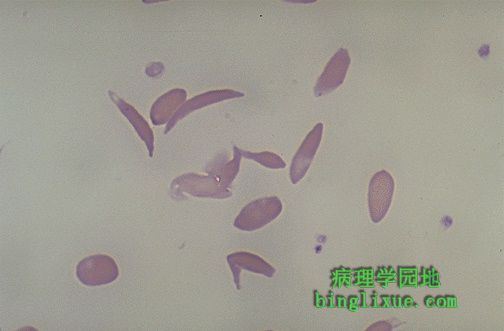
镰状细胞危象中出现严重的腹痛,可见具有血红蛋白SS的镰状红细胞。镰状细胞易于粘连在一起,堵塞小血管,血流减少而导致局部缺血。 Here is another example of sickled erythrocytes in a patient with Hgb SS who presented with severe abdominal pain in sickle crisis. The sickled cells are prone to stick together, plugging smaller vessels and leading to decreased blood flow with ischemia. |
 |
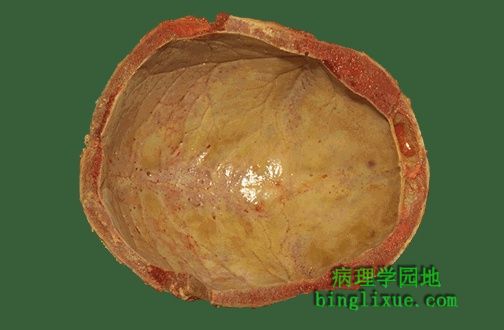
虽然在儿童早期镰状细胞贫血可导致脾增大,但在青春期由于异常的RBC持续的郁积和阻塞,引起脾梗死,脾体积明显缩小。有时称为做“自体脾切除”。如图可见镰状细胞贫血患者残存的小脾脏。 Though in early childhood the spleen may be enlarged with sickle cell anemia, continual stasis and trapping of abnormal RBC's leads to infarctions that eventually reduce the size of the spleen tremendously by adolescence. This is sometimes called "autosplenectomy". Seen here is the small remnant of spleen in a patient with sickle cell anemia. |
 |
严重贫血病人输血后的全血细胞计数。下的红细胞直方图显示双峰。另外,因贫血而引起的网织红细胞增多使MCV(红细胞平均体积)增加。 Here is the CBC of a person with a severe anemia who underwent transfusion. This accounts for the dual RBC population as seen in the graph at the lower left. A reticulocytosis in response to anemia has also increased the MCV. |
 |
严重的慢性贫血症(如地中海贫血症和镰状细胞贫血症)可增强骨髓生成RBC的能力,促进骨髓增生,使骨髓所在部位发生变化,如图可见异常的颅骨,骨髓增生使颅骨形状发生变化(前额隆起或额头突出)。 Severe, chronic anemias (such as thalassemias and sickle cell anemia) can increase the bone marrow response to form RBC's. This drive for erythropoiesis may increase the mass of marrow and lead to increase in marrow in places, such as the skull seen here, that is not normally found. Such an increase in marrow in skull may lead to "frontal bossing" or forehead prominence because of the skull shape change. |
 |
血红蛋白SC病同明有血红蛋白S和血红蛋白S的存在,RBC可能呈镰状,但不如血红蛋白SS那样常见。血红蛋白C导致靶细胞(红细胞)中心略带红色。视野中心可见一矩形红细胞(因血红蛋白C晶体存在),也是血红蛋白C病的特征。 This patient has hemoglobin SC disease, with hemoglobin S and hemoglobin C both present. With SC disease, the RBC's may sickle, but not as commonly as with Hemoglobin SS disease. The hemoglobin C leads to the formation of "target" cells--RBC's that have a central reddish dot. In the center of the field is a rectangular RBC that is indicative of a hemoglobin C crystal, which is also characteristic for hemoglobin C disease. |
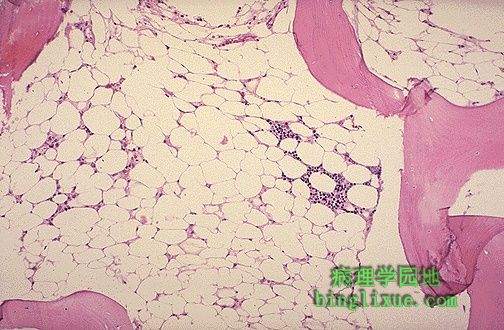 |
再生障碍性贫血骨髓活检可见造血成分明显减少,除此之外,网织红细胞和粒细胞通常减少。病因可能是是药物或毒物,有时是感染。不明原因的称为先天性再生障碍性贫血。 Hematopoietic elements in this bone marrow biopsy are markedly reduced. This is a case of aplastic anemia. Of course, besides, RBC's the platelets and granulocytes will often be diminished. Sometimes a drug or toxin is the cause and sometimes infection. When no known cause can be found, it is termed idiopathic aplastic anemia. |
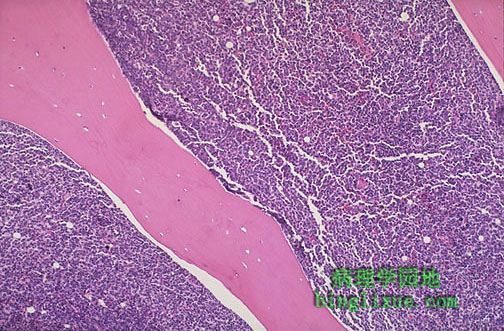 |
与再生障碍性贫血不同,白血病的结果是骨髓有大量细胞。如图可见粉红色的骨小梁之间的骨髓几乎100 %是细胞,是由急性淋巴母细胞性白血病(ALL)的白血病细胞构成,这些细胞实际上替代或抑制了正常的造血作用。虽然骨髓有非常多的细胞,但外周血细胞减少。这就解释了白血病的并发症感染(缺乏正常的白细胞)、出血(缺乏血小板)和、贫血(缺乏红细胞)的原因。 In contrast to aplastic anemia, leukemia results in a highly cellular marrow. The marrow between the pink bone trabeculae seen here is nearly 100% cellular, and it consists of leukemic cells of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) that have virtually replaced or suppressed normal hematopoiesis. Thus, though the marrow is quite cellular, there can be peripheral cytopenias. This explains the complications of infection (lack of normal leukocytes), hemorrhage (lack of platelets), and anemia (lack of red blood cells) that often appear with leukemia. |
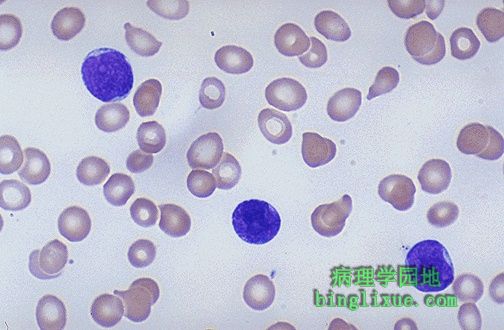 |
白血病可见白细胞是淋巴细胞,但它们是母细胞--核中含有核仁的、更大的、非常不成熟的细胞。这样的淋巴细胞提示急性淋巴母细胞性白血病(ALL)的存在。ALL在儿童中比成年人常见。 儿童中的ALL很多治疗在效,并且可以治愈。 The WBC's seen here are lymphocytes, but they are blasts--very immature cells with larger nuclei that contain nucleoli. Such lymphocytes are indicative of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). ALL is more common in children than adults. Many cases of ALL in children respond well to treatment, and many are curable. |
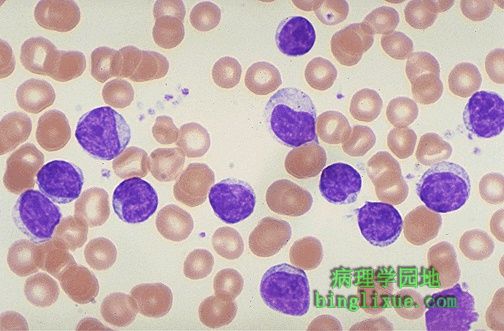 |
成熟的淋巴细胞在数量上明显增加,提示慢性淋巴细胞性白血病,最常在年龄较大的成年人中出现。治疗效果很差,但发展缓慢。 These mature lymphocytes are increased markedly in number. They are indicative of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, a disease most often seen in older adults. This disease responds poorly to treatment, but it is indolent. |
 |
非常大的、多核的、未成熟的髓母细胞,这些细胞中可见典型的线性红色Auer小体。主要发生于急性髓母细胞白血病(AML),年轻人多见。 Here are very large, immature myeloblasts with many nucleoli. A distincitve feature of these blasts is a linear red "Auer rod" composed of crystallized granules. These findings are typical for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) that is most prevalent in young adults. |