
 |
镜下微脓肿。中心可见由蓝色菌落组成,并且为急性炎症细胞所包围。 The microscopic appearance of a microabscess is shown here. The center consists of blue bacterial colonies and is surrounded by acute inflammatory cells. |
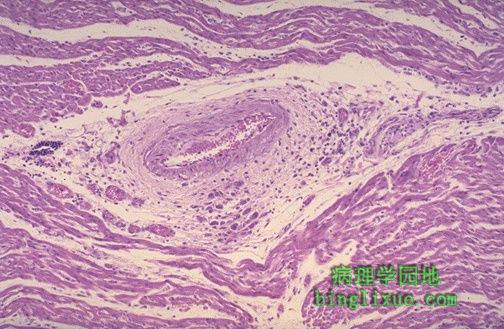 |
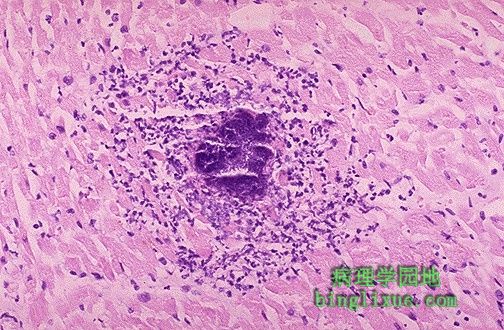
显微镜下可清楚地见到特殊的炎性肉芽肿形态(被称为Aschoff小体),急性风湿性心脏炎的特征。肉芽肿多发生在血管周围的间质中。严重的心肌炎可能导致充血性心力衰竭。 Microscopically, acute rheumatic carditis is marked by a peculiar form of granulomatous inflammation with so-called "Aschoff nodules" seen best in myocardium. These are centered in interstitium around vessels as shown here. The myocarditis may be severe enough to cause congestive heart failure. |
 |
高倍镜下的Aschoff小体。它组成成份是风湿细胞,体积大,可有双核或多核(核仁很明显)。旁边可见散在的炎性细胞,其中有单核细胞或有时可见嗜中性粒细胞。 Here is an Aschoff nodule at high magnification. The most characteristic component is the Aschoff giant cell. Several appear here as large cells with two or more nuclei that have prominent nucleoli. Scattered inflammatory cells accompany them and can be mononuclears or occasionally neutrophils. |
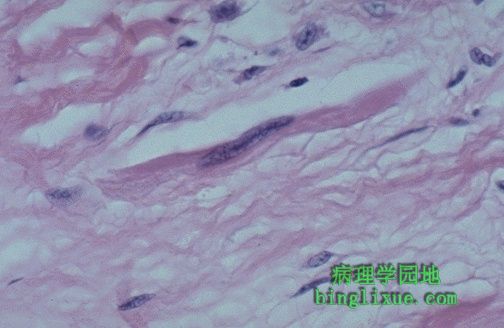 |
可见急性风湿性心脏炎时另一种特殊的细胞:Anitschkow 肌细胞。它又细又长,有一个长梭形细胞核。 Another peculiar cell seen with acute rheumatic carditis is the Anitschkow myocyte. This is a long, thin cell with an elongated nucleus. |
 |
慢性风湿性心瓣膜病可能由急性心内膜炎机化和纤维化发展而来,可见二尖瓣受到影响。注意腱索缩短和变厚了。 In time, chronic rheumatic valvulitis may develop by organization of the acute endocardial inflammation along with fibrosis, as shown here affecting the mitral valve. Note the shortened and thickened chordae tendineae. |
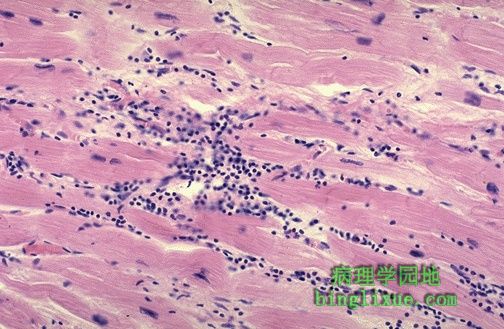 |
病毒心肌炎可能是最常见的一种心肌炎,其特征性表现是间质淋巴细胞的浸润。许多病毒心肌炎临床表现不明显,有些可能导致青年人猝死。心肌很少坏死。最常用的病毒是柯萨奇病毒B。 The interstitial lymphocytic infiltrates shown here are characteristic for a viral myocarditis, which is probably the most common type of myocarditis. Many of these cases are probably subclinical. Some may be a cause for sudden death in young persons. There is usually little necrosis. The most common viral agent is Coxsackie B. |
 |
两岁小儿猝死。尸检发现一个大而坚硬的白色肿瘤占了左心室的大部分。是横纹肌瘤。这种心脏原发瘤罕见。 This two year old child died suddenly. At autopsy, a large firm, white tumor mass was found filling much of the left ventricle. This is a cardiac rhabdomyoma. Such primary tumors of the heart are rare. |
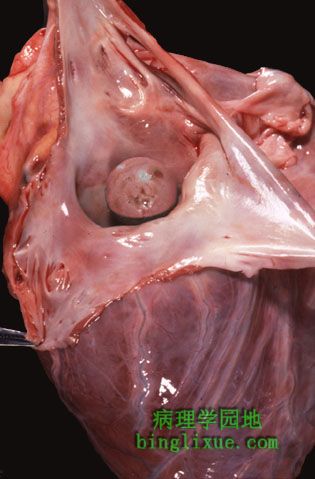 |
从剖开的左心房可见最为普遍的原发性心脏肿瘤-心房粘液瘤。这些良性肿块大多附着在心房壁上,但也可以在瓣膜或心室出现。他们可以产生“球阀”效应,引起房室瓣口间歇性关闭。肿块的碎片也可能引发栓塞。超声心动图可容易诊断粘液瘤。 The left atrium has been opened to reveal the most common primary cardiac neoplasm--an atrial myxoma. These benign masses are most often attached to the atrial wall, but can arise on a valve or in a ventricle. They can produce a "ball valve" effect by intermittently occluding the atrioventricular valve orifice. Embolization of fragments of tumor may also occur. Myxomas are easily diagnosed by echocardiography. |
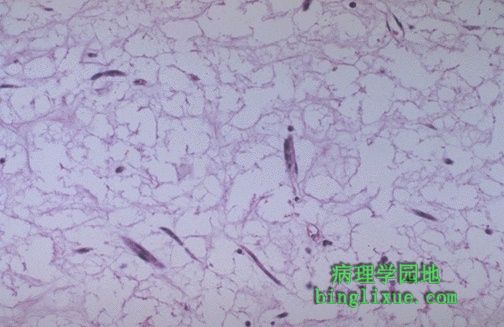 |
高倍镜可见心房粘液瘤极小的细胞结构,仅有散在的纺锤形细胞,在疏松的粘液样基质中有少量淡红的胞浆存在。 This high power microscopic appearance of cardiac myxoma shows minimal cellularity. Only scattered spindle cells with scant pink cytoplasm are present in a loose myxoid stroma. |
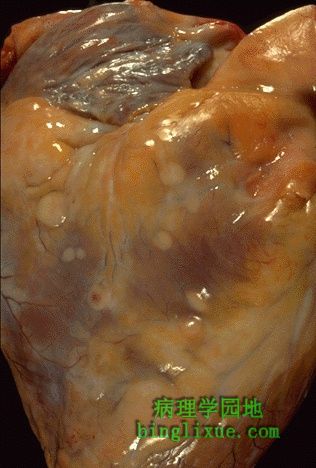 |
心脏原发瘤少见,继发瘤相对多见,但总体而言,还是较少见的(在所有恶性肿瘤中,仅有大约5%~10%的发生心脏转移)。在心外膜的表面可见灰白色转移性肿瘤结节。转移性肿瘤可导致出血性心包炎。 Primary tumors of the heart are uncommon. Metastases to the heart are more common, but rare overall (only about 5 to 10% of all malignancies have cardiac metastases). Seen over the surface of the epicardium are pale white-tan nodules of metastatic tumor. Metastases may lead to a hemorrhagic pericarditis. |