
 |
马凡综合征二尖瓣,见小叶增大, 在左方远处的一个小叶向上隆起。这是二尖瓣脱垂的特点。固定小叶的腱索变得细长。体格检查时发现的收缩中期期卡嗒音为其特征表现。 The mitral valve is shown in the same patient with Marfan's syndrome. The leaftlets of the mitral valve are redundant, and the one on the far left is ballooned upward. This is characteristic of floppy mitral valve with mitral valve prolapse. The chordae tendineae that hold the leaflets become long and thin. The characteristic finding on physical exam is a mid-systolic click. |
 |
马凡综合征患者二尖瓣可见左下方的小叶向上隆起,二尖瓣脱垂导致顶端的小叶(此区已变为红黑色)挫伤。 This view of the mitral valve in a patient with Marfan's syndrome depicts a floppy mitral valve. The leaflet on the lower left has ballooned upward and the prolapse has resulted in contusion of the top of the leaflet, with a red black area of discoloration. |
 |
经过粘蛋白染色的主动脉壁可见囊状中层坏死,这不仅是马凡综合征的表现,度且从动脉切面可见结缔组织薄弱,导致主动脉剥离。正常的平行排列的粉红色弹性纤维被染成蓝色的粘液样物质破坏。 This mucin stain of the wall of the aorta demonstrates cystic medial necrosis, typical for Marfan's syndrome and causes the connective tissue weakness that explains the aortic dissection. Pink elastic fibers, instead of running in parallel arrays, are disrupted by pools of blue mucinous ground substance. |
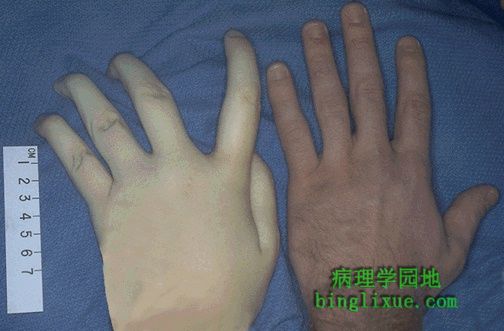 |
左为马凡综合征年轻女性的手,右为正常女性的手。两人身高均为188厘米,注意不同的是,左边的手有蜘蛛样指。 The hand at the left is that of a young woman with Marfan's syndrome, while the hand at the right is a normal male. Both persons were of the same height, 188 cm. However, note that the hand at the left demonstrates arachnodactyly. |
 |
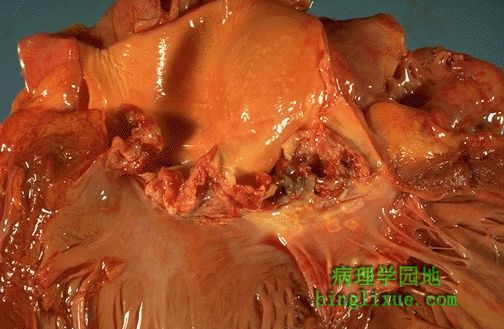
感染性心内膜炎:见主动脉瓣处有一大而不规则的红褐色赘生物。毒力强的细菌,如金黄*色葡萄球菌,引起“性细菌性心内膜炎,而一些毒力较弱的细菌,如草绿色链球菌,则引起亚急性细菌性心内膜炎。 This is infective endocarditis. The aortic valve demonstrates a large, irregular, reddish tan vegetation.Virulent organisms, such as Staphylococcus aureus, produce an "acute" bacterial endocarditis, while some organisms such as Streptococcus viridans produce a "subacute" bacterial endocarditis. |
 |
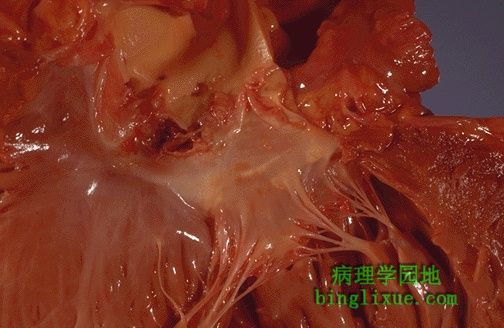
主动脉瓣示,毒力强的细菌可引发急性感染性心内膜炎,从而导致心脏严重损坏。红棕色的赘生物覆盖瓣膜尖端使其受损,赘生物的一部分可以脱落形成脓性栓子。 The more virulent bacteria causing the acute bacterial form of infective endocarditis can lead to serious destruction, as shown here in the aortic valve. Irregular reddish tan vegetations overlie valve cusps that are being destroyed. Portions of the vegetation can break off and become septic emboli. |
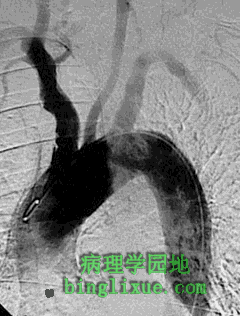 |
血管造影显示主动脉弓和大动脉。主动脉瓣的赘生物脱落形成栓子进入血液循环。图示感染性心内膜炎时脓毒性栓子通过左颈动脉引起栓塞,导致脑梗死和(或)脑脓肿。 This angiogram demonstrates the aortic arch and great vessels. An embolus from a cardiac valvular vegetation from the left side of the heart can travel out the systemic circulation. Shown here is a septic embolus from infective endocarditis travelling up the left common carotid artery, which could result in a cerebral infarction and/or abscess. |
 |
感染性心内膜炎显示了源自瓣膜表面的感染的传播途径。可见心内膜表面的赘生物,并且感染蔓延到下面的心肌。 In this case, the infective endocarditis demonstrates how the infection tends to spread from the valve surface. Here, vegetations can be seen on the endocardial surfaces, and the infection is extending into to underlying myocardium. |
 |
二尖瓣的感染性心内膜炎已蔓延到三尖瓣的隔膜、并穿孔。 Here, infective endocarditis on the mitral valve has spread into the septum all the way to the tricuspid valve, producing a fistula. |
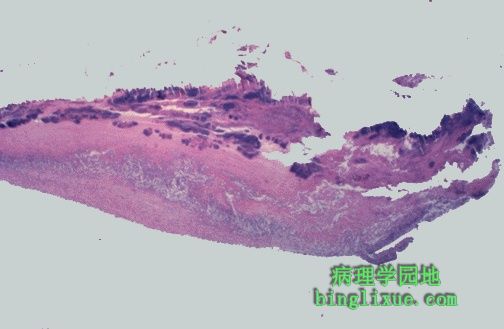 |
显微镜下可见感染性心内膜炎瓣膜覆盖松脆的赘生物,其中有纤维蛋白和血小板(淡红色),并夹杂着炎性细胞和菌落(蓝色)。由于赘生物的易碎,因此极易脱落和引起栓塞。 Microscopically, the valve in infective endocarditis demonstrates friable vegetations of fibrin and platelets (pink) mixed with inflammatory cells and bacterial colonies (blue). The friability explains how portions of the vegetation can break off and embolize. |