
 |
青霉素过敏时出现急性喉头水肿而致死。 为I型超敏反应,肥大细胞上的IgE抗体与抗原反应,肥大细胞快速释放组胺和其它介质致水肿发生。 The acute laryngeal edema seen here that killed the patient was due to an anaphylactic reaction to penicillin. Such an allergy is a form of type I hypersensitivity reaction in which there is preformed IgE antibody on mast cells that quickly reacts with an antigen. The mast cells release histamine and other mediators that lead to the edema. |
 |
病人除黄疸外,还有明显的鳞屑。这个病人进行了骨髓移植,其中6个抗原有5个相配。此为移植物抗宿主反应,供者淋巴细胞攻击了宿主组织。 Besides the icterus (yellow color, jaundice) in this skin there is a fine scaling rash in this patient following bone marrow transplantation with a 5 out of 6 antigen match. This is an example of graft versus host disease in which donor lymphocytes attack host tissues. |
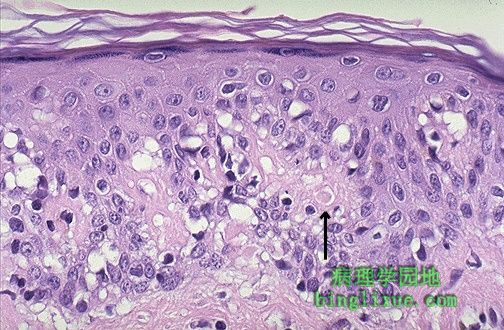 |
镜下,移植物抗宿主反应是说明“程序性细胞死亡”或单个细胞坏死(即调亡)过程的最好例子。在基底层有上皮细胞的空泡形成或溶解,并伴淋巴细胞浸润。箭头示粉红色的凋亡小体。 Microscopically, graft versus host disease is one of the best examples of a process called "apoptosis" or single cell necrosis. There is vacuolization and dissolution of epidermal cells along the basal layer, along with lymphocytes. At the arrow is a rounded pink apoptotic body. |
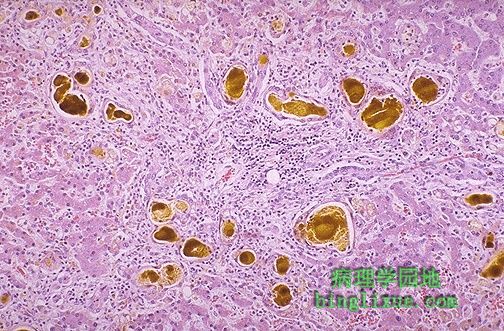 |
移植物抗宿主病导致明显的肝内胆汁郁积。可见大量的黄*色胆汁淤积在胆小管内. Graft versus host disease also leads to marked cholestasis in the liver, seen here as large collections of yellow-green bile pigment in the bile canaliculi. |
 |
移植物抗宿主疾病反映的是胆小管内黄棕色的胆汁淤积,同时肝实质慢性炎细胞浸润。 The graft versus host disease here is marked by yellow-brown collections of bile in the canaliculi, as well as chronic inflammatory cells within the liver parenchyma. |
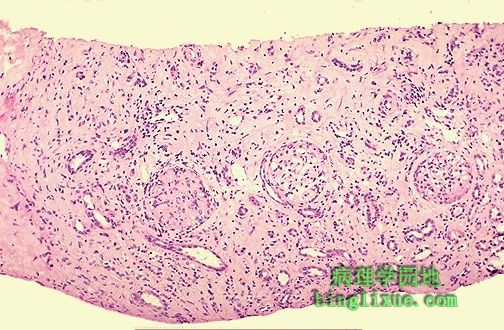 |
免疫疾病往往使实质脏器移植变得复杂。图示慢性血管排斥病人肾活检见间质纤维化. Immunologic disease can also complicate solid organ transplantation. Here is a renal biopsy that demonstrates marked interstitial fibrosis in a patient with chronic vascular rejection. |
 |
高倍镜下,慢性血管排斥反应引起肾动脉显著增厚和纤维化。出现间质纤维化和慢性炎症,慢性排斥反应通常在移植后数月到数年缓慢发生,不象急性排斥反应且难于治疗。 At high magnification, the renal arteries with chronic vascular rejection are markedly thickened and fibrotic. There is interstitial fibrosis and chronic inflammation. Such chronic rejection usually occurs slowly over several months to years following transplantation. This disease, unlike acute rejection, is difficult to treat. |
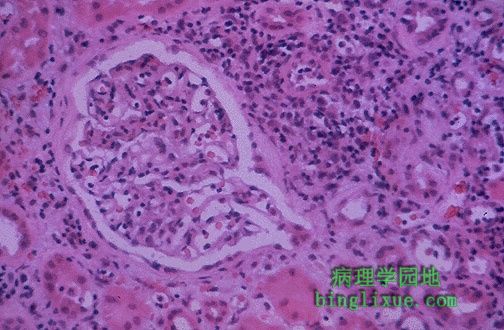 |
急性肾移植排斥反应,大多数的炎症发生在间质,肾小球正常,但肾小管被右上方的许多淋巴细胞浸润。 This is a form of acute renal transplant rejection known as acute cellular tubulointerstitial rejection because most of the inflammation is in the interstitium. The glomerulus seen here is normal, but the tubules are infiltrated by many lymphocytes at the upper right. |
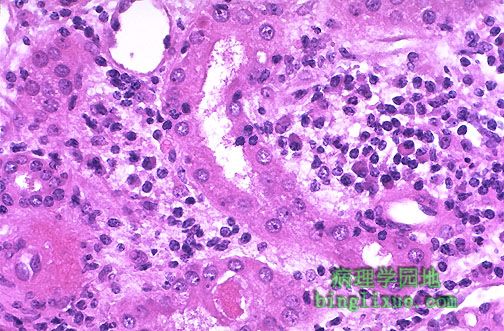 |
高倍镜可见发生急性细胞排斥反应的肾移植病人的淋巴细胞和浆细胞浸润于肾小管周围。可发生于肾移植的任何时候,尤其当免疫抑制剂减弱的时候。可通过给予环胞霉素和其它免疫抑制剂治疗。 At high magnification, the lymphocytes and plasma cells are seen around a renal tubule in a renal transplant patient with acute cellular rejection. This type of rejection can occur at any time following transplantation when immunosuppression is diminished. This is treated by administering cyclosporine and other immunosuppressive agents. |
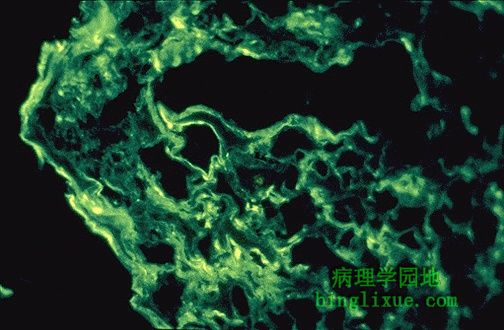 |
免疫荧光镜下示肾移植后急性肾小管间质性排斥反应。免疫沉积物出现在肾小球间。II型和IV型超敏反应促进了排斥反应的发生。 The immunofluorescence pattern with acute tubulointerstitial renal transplant rejection is shown here, in which immune deposits occur between glomeruli in the interstitium. Both type II and type IV immune hypersensitivity reactions contribute to this rejection reaction. |