
 |
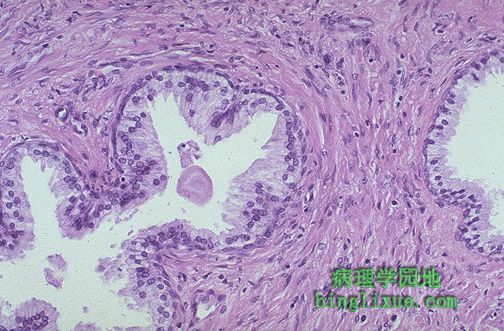
高倍镜示正常前列腺和周围的肌纤维间质。一粉红色的凝固物(在正常的前列腺体中能见到的典型的淀粉小体)正好出现在腺体中央的左侧。可见在分化良好的腺体中有高柱状的排列整齐的上皮细胞。这些细胞的核仁不显著。 The normal histologic appearance of prostate glands and surrounding fibromuscular stroma is shown here at high magnification. A small pink concretion (typical of the corpora amylacea seen in benign prostatic glands) appears in the gland just to the left of center. Note the well-differentiated glands with tall columnar epithelial lining cells. These cells do not have prominent nucleoli. |
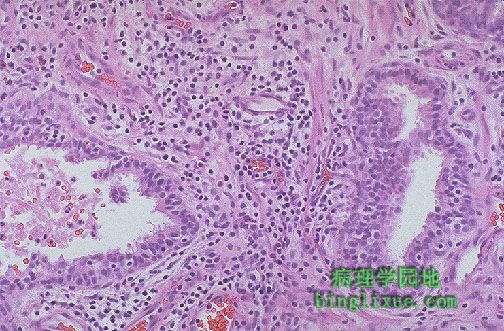 |
慢性前列腺炎。腺体间的间质中可见大量小的深蓝色的淋巴细胞。可伴有细菌感染,也可同时伴有膀胱炎或尿道炎。然而慢性前列腺炎多为细菌性,且没有泌尿道感染史。血清中前列腺特异抗原可轻微升高。 This is chronic prostatitis. Numerous small dark blue lymphocytes are seen in the stroma between the glands. There may be a bacterial agent accompanying this inflammation, and cystitis or urethritis may also be present. However, more commonly, chronic prostatitis is abacterial and there is no history of urinary tract infection. The serum prostate specific antigen may be slightly elevated. |
 |
正常前列腺直径约3-4cm。前列腺结节状增生致体积增大,称为BPH(良性前列腺增生)或结节状前列腺增生。 A normal prostate gland is about 3 to 4 cm in diameter. This prostate is enlarged due to prostatic hyperplasia, which appears nodular. Thus, this condition is termed either BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or nodular prostatic hyperplasia. |
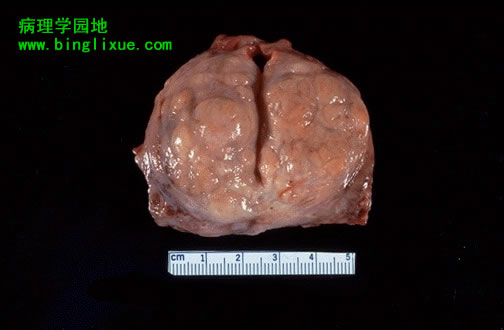 |
另例良性前列腺增生,小结节主要出现于侧叶。这样增大的前列腺阻碍尿液从膀胱流出,进而引起尿道梗阻性疾病。 Here is another example of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Nodules appear mainly in the lateral lobes. Such an enlarged prostate can obstruct urinary outflow from the bladder and lead to an obstructive uropathy. |
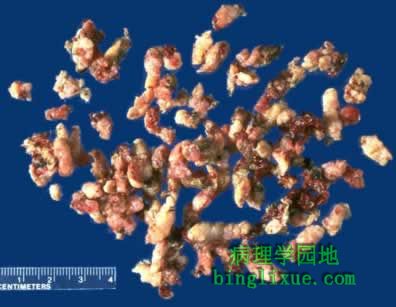 |
经尿道前列腺切除(TURP)术是良性前列腺增生的主要治疗手段。图为切除的前列腺碎片。 A frequently performed operation for symptomatic nodular prostatic hyperplasia is a transurethral resection, which yields the small "chips" of rubbery prostatic tissue seen here. |
 |
增生的前列腺不仅侧叶增大,中叶也增大,并且阻塞了尿道前列腺部。从膀胱壁粘膜表面明显的小梁形成可以看出阻塞使膀胱肥大。伴有尿液郁积的阻塞还能导致黄褐色的结石(石头)形成。 The enlarged prostate gland seen here not only has enlarged lateral lobes, but also a greatly enlarged median lobe that obstructs the prostatic urethra. This led to obstruction with bladder hypertrophy, as evidenced by the prominent trabeculation of the bladder wall seen here from the mucosal surface. Obstruction with stasis also led to the formation of the yellow-brown calculus (stone). |
 |
结节性前列腺增生引起的阻塞致显著的小梁形成,可在过度增生的膀胱粘膜表面见到。阻塞导致的郁积易于引起感染, 同时阻塞还能引起双侧的输尿管积水和肾盂积水。 Obstruction from nodular prostatic hyperplasia has led to prominent trabeculation seen on the mucosal surface of this bladder with hypertrophy. The stasis from obstruction predisposes to infection. The obstruction can also lead to bilateral hydroureter and hydronephrosis. |
 |
显微镜下,虽然前列腺体增生时腺体增生更突出,但也包括间质增生。图示巨大增生结节的腺体。 Microscopically, benign prostatic hyperplasia can involve both glands and stroma, though the former is usually more prominent. Here, a large hyperplastic nodule of glands is seen. |
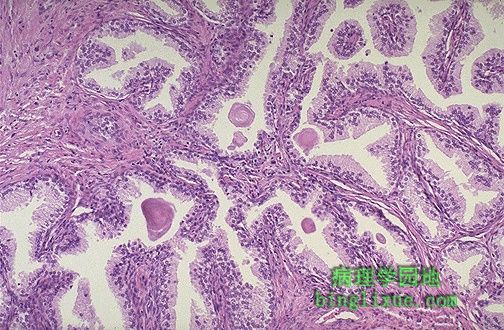 |
高倍镜示增生前列腺的腺体增生。分化较好的腺体间有间质分布。腺腔内可见粉红色层状的淀粉样小体。 At higher magnification, the enlarged prostate has glandular hyperplasia. The glands are well-differentiated and still have some intervening stroma. The small laminated pink concretions within the glandular lumens are known as corpora amylacea. |
 |
前列腺上皮内瘤变(PIN),可在单个腺泡或小群腺泡中见到的非典型增生。PIN的分化级可高可低。PIN的发现提示前列腺癌可能存在(约半数伴有高分级PIN)。 This is prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN), a precancerous cellular proliferation found in a single acinus or small group of acini. PIN can be low or high grade (as seen here). The finding of PIN suggests that prostatic adenocarcinoma may also be present (about half the time with high grade PIN). |