
 |
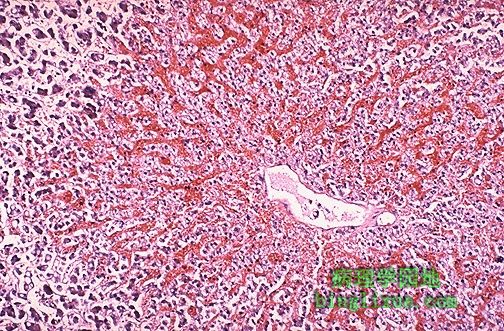
镜下可见,中央静脉周围淤血导致槟榔样表现,病因一般为右心衰。 Microscopically, the nutmeg pattern results from congestion around the central veins, as seen here. This is usually due to a "right sided" heart failure. |
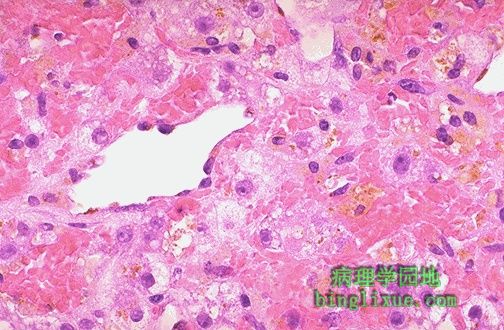 |
如果淤血显著,由于肝小叶3区(位于中央静脉周围)血液含氧量不足,将发生肝小叶中心坏死。图中中央静脉周围坏死肝细胞中的浅褐色色素为脂褐素。 If the passive congestion is pronounced, then there can be centrilobular necrosis, because the oxygenation in zone 3 of the hepatic lobule is not great. The light brown pigment seen here in the necrotic hepatocytes around the central vein is lipochrome. |
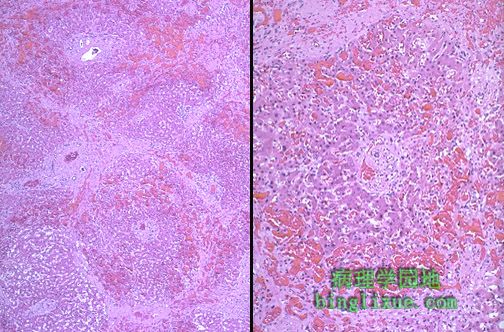 |
如果慢性肝脏淤血持续时间较长,如图示,中央静脉之间出现纤维桥接,发生“心源性肝硬化”,因此门管区位于重建的肝小叶(假小叶)中央。最好称为“心源性肝硬化”,因为它不同于真正的肝硬化,很少有肝细胞结节状再生。 If chronic hepatic passive congestion continues for a long time, a condition called "cardiac cirrhosis" may develop in which there is fibrosis bridging between central zonal regions, as shown below, so that the portal tracts appear to be in the center of the reorganized lobule. This process is best termed "cardiac sclerosis" because, unlike a true cirrhosis, there is minimal nodular regeneration. |
 |
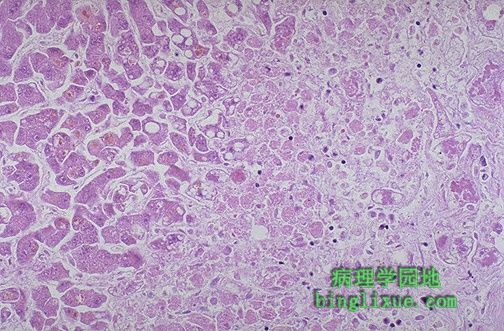
图中右侧见多个肝脏梗死灶。由于肝脏具有双重血液供应—门静脉和肝动脉,因此很少梗死。图中的梗死灶为黄*色,境界清楚,周围是充血带。大约一半的肝脏梗死出现于动脉炎时,其余半数的病因多样。 At the right are seen several infarcts of the liver. Infarcts are uncommon because the liver has two blood supplies-portal venous system and hepatic arterial system. The infarcts seen here are yellow, with geographic borders and surrounding hyperemia. About half of liver infarcts occur with arteritis, and the remaining half are due to a variety of causes. |
 |
药物对乙酰氨基酚(退热净)使用过量患者表现为广泛的肝细胞坏死。右侧的肝细胞已经死亡,左侧的濒临死亡。这种表现可见于多种肝脏中毒时。急性肝功能衰竭可导致肝性脑病。 There is extensive hepatocyte necrosis seen here in a case of acetaminophen overdose. The hepatocytes at the right are dead, and those at the left are dying. This pattern can be seen with a variety of hepatotoxins. Acute liver failure leads to hepatic encephalopathy. |
 |
显性遗传性多囊肾(DPKD)患者的肝脏中具有大量包囊。本病发病于成年,并在中年时发生肾衰。多囊改变有时也可影响肝脏(如图所示)。胰腺很少受累。DPKD患者还可发生脑动脉的小动脉瘤。 Numerous cysts appear in this liver from a patient with dominant polycystic kidney disease (DPKD). Such cases occur in adults and manifest with renal failure beginning in middle age. Sometimes the liver (as seen here) can be affected as well by polycystic change. Less commonly the pancreas is involved. These patients with DPKD can also have berry aneurysms in the cerebral arteries. |
 |
CT显示肝实质多个较大包囊,与显性遗传性多囊肾病人的肝脏病变相一致。 This transverse CT scan of the liver demonstrates multiple large cysts in the parenchyma, consistent with polycystic change in the liver of a patient with dominant polycystic kidney disease. |
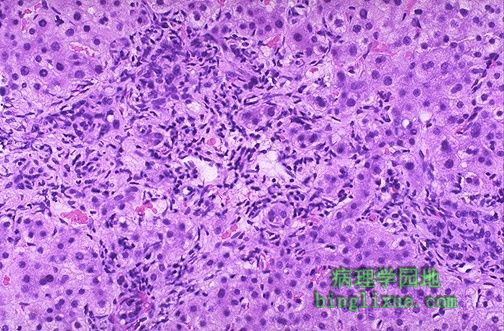 |
原发性胆汁性肝硬化是一种少见的自身免疫性疾病(多见中年妇女),表现为肝脏三联管(小叶间动脉、小叶间静脉、小叶间胆管)中的小叶间胆管破坏。患者血清中可检测到抗线粒体抗体。图中的门管区具有突出的慢性炎性浸润而胆小管丧失。随后可发生小结节性肝硬化。 This is a case of primary biliary cirrhosis, a rare autoimmune disease (mostly of middle-aged women) that is characterized by destruction of bile ductules within the triads of the liver. Antimitochondrial antibody can be detected in serum. Seen here in a portal tract is an intense chronic inflammatory infiltrate with loss of bile ductules. Micronodular cirrhosis ensues. |
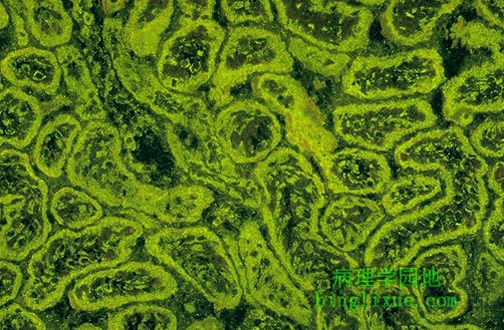 |
抗线粒体抗体(AMA)与原发胆汁性肝硬化相关。该实验的组织底物为肾实质,AMA免疫荧光显示小胆管细胞内具有大量亮绿色的线粒体。 This immunofluorescence pattern is positive for anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA) which has an association with primary biliary cirrhosis. The tissue substrate for this test is renal parenchyma, and the tubule cells have lots of mitochondria, which stain bright green. |
 |
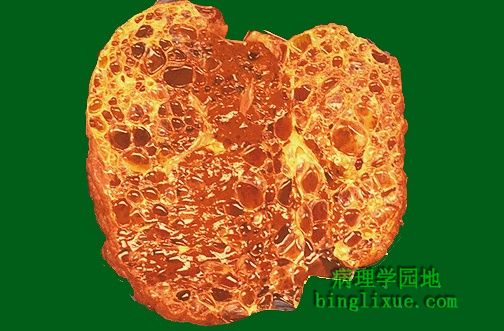
肝外胆道闭锁为肝脏或胆总管的狭窄与炎症,这是一例死于肝外胆道闭锁的3个月婴儿。该病导致显著的胆汁淤积和肝内胆管增生、纤维化、肝硬化。肝脏如岩石般坚硬。福尔马林作用于发生显著胆汁淤积的肝脏中的胆色素,将胆红素转化为胆绿素而呈暗绿色。 This 3 month old child died with extrahepatic biliary atresia, a disease in which there is inflammation with stricture of hepatic or common bile ducts. This leads to marked cholestasis with intrahepatic bile duct proliferation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. This liver was rock hard. The dark green color comes from formalin acting on bile pigments in the liver from marked cholestasis, turning bilrubin to biliverdin. |