
 |
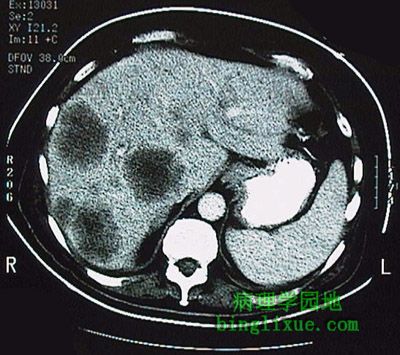
腹部横断面CT显示肝脏多发性肿块,属结肠腺癌转移性病变。图右下(病人左侧)可见正常脾。 This computed tomographic (CT) scan with contrast of the abdomen in transverse view demonstrates multiple mass lesions representing metastases from a colonic adenocarcinoma. A normal spleen appears at the lower right in the image (on the patient's left). |
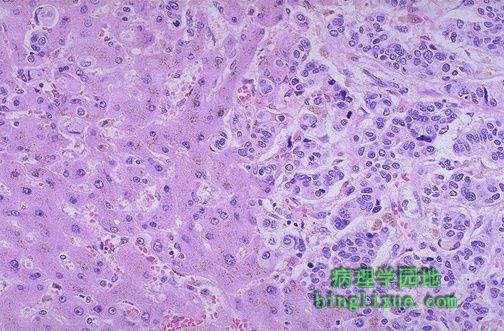 |
镜下可见,右侧为乳腺浸润性导管癌的转移灶,左侧为正常肝实质。 Microscopically, metastatic infiltrating ductal carcinoma from breast is seen on the right, with normal liver parenchyma on the left. |
 |
肉眼可见坏死区域和肝小叶结构崩解,表现为淡黄*色的模糊区域。肝炎时发生这种坏死。 Grossly, there are areas of necrosis and collapse of liver lobules seen here as ill-defined areas that are pale yellow. Such necrosis occurs with hepatitis. |
 |
坏死和小叶崩解表现为肝脏切面上的出血、不规则的凹陷和突起。 The necrosis and lobular collapse is seen here as areas of hemorrhage and irregular furrows and granularity on the cut surface of the liver. |
 |
病毒性肝炎导致肝细胞破坏。单核细胞浸润从门脉区延伸,破坏正在坏死(也称为慢性活动性肝炎的“碎片状”坏死)的肝细胞界板。该患者的乙肝表面抗原(HbsAg)和乙肝核心抗体(HbcAb)呈阳性。 Viral hepatitis leads to liver cell destruction. A mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate extends from portal areas and disrupts the limiting plate of hepatocytes which are undergoing necrosis, the so-called "piecemeal" necrosis of chronic active hepatitis. In this case, the hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) and hepatitis B core antibody (HbcAb) were positive. |
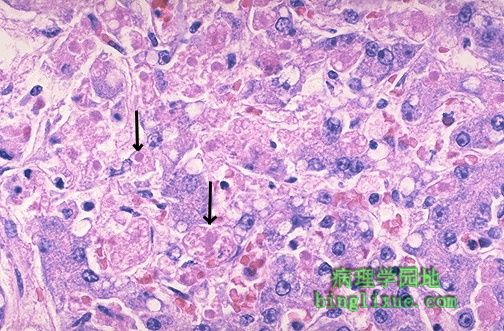 |
病毒性肝炎单个肝细胞受累。甲肝很少引起显著的坏死,但乙肝能够导致广泛肝细胞坏死的爆发型肝炎。右侧箭头下方,大的粉红色细胞正在发生“气球样变”。进一步发展,如左侧箭头所示,濒临死亡的肝细胞正浓缩形成嗜酸性小体。 Individual hepatocytes are affected by viral hepatitis. Viral hepatitis A rarely leads to signficant necrosis, but hepatitis B can result in a fulminant hepatitis with extensive necrosis. A large pink cell undergoing "ballooning degeneration" is seen below the right arrow. At a later stage, a dying hepatocyte is seen shrinking down to form an eosinophilic "councilman body" below the arrow on the left. |
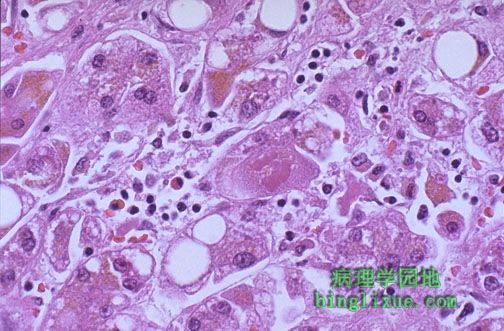 |
丙型肝炎,有一半丙肝可发展为慢性。慢性肝炎通过活动程度(坏死与炎症)分级,通过纤维化程度分期。该患者的坏死和炎症显著,伴一定程度的脂肪变性。不管肝炎的分期和分级如何,病因是必须要查明的,因为治疗需要明确的病因,并且而不同病因的慢性肝炎可表现为相似的镜下和肉眼病变。 This is a case of viral hepatitis C, which in half of cases leads to chronic liver disease. The extent of chronic hepatitis can be graded by the degree of activity (necrosis and inflammation) and staged by the degree of fibrosis. In this case, necrosis and inflammation are prominent, and there is some steatosis as well. Regardless of the grade or stage, the etiology of the hepatitis must be sought, for the treatment may depend upon knowing the cause, and chronic liver diseases of different etiologies may appear microscopically and grossly similar. |
 |
广泛纤维化并进展为大结节性肝硬化的丙型肝炎,右中部即为大的再生结节。目前,诊断该型病毒性肝炎的唯一实验室检查为丙肝抗体实验。从前称为“非甲非乙型肝炎”中的大部分(但不是全部)病例为丙肝。 This is a case of viral hepatitis C which is at a high stage with extensive fibrosis and progression to macronodular cirrhosis, as evidenced by the large regenerative nodule at the center right. At present, the sole laboratory test for identification of this form of viral hepatitis is the hepatitis C antibody test. Hepatitis C accounts for most (but not all) cases formerly called "non-A, non-B hepatitis". |
 |
三色染色显示病毒性肝炎时肝实质塌陷。蓝染区域为同时塌陷的许多门管区的结缔组织。 This trichrome stain demonstrates the collapse of the liver parenchyma with viral hepatitis. The blue-staining areas are the connective tissue of many portal tracts that have collapsed together. |
 |
慢性肝淤血时的槟榔肝。暗红色淤血区表示肝小叶中心区的红细胞积聚。 Here is an example of a "nutmeg" liver seen with chronic passive congestion of the liver. Note the dark red congested regions that represent accumulation of RBC's in centrilobular regions. |