
 |
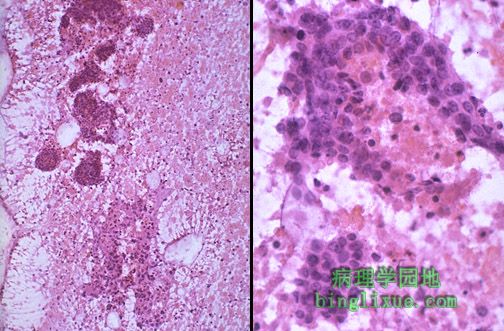
针吸(FNA)细胞学对诊断可触知与乳腺X射线造影术可发现的乳腺病变而言是一项有用的技术。左边可见低倍放大的松散的细胞群;右边可见高倍放大的癌的异型核特征。 Fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology is a useful technique for diagnosis of palpable and mammographically detectable breast lesions. Seen on the left at low magnification are discohesive clusters of cells; on the right at high magnification the atypical nuclei characteristic for a carcinoma are present. |
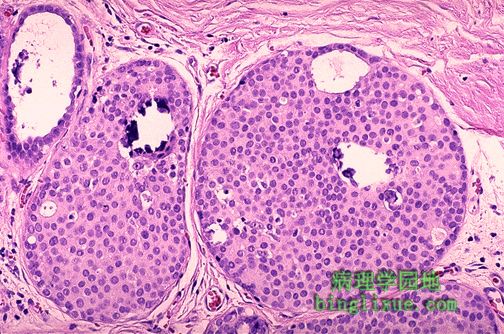 |
导管内癌高倍放大图。肿瘤细胞位于导管上皮内且没有穿透基底膜至间质。值得注意的是中央处两个大的小叶包含了小钙化灶。这种钙化在乳腺X射线造影术下可见。 This high power microscopic view demonstrates intraductal carcinoma. Neoplastic cells are still within the ductules and have not broken through into the stroma. Note that the two large lobules in the center contain microcalcifications. Such microcalcifications can appear on mammography. |
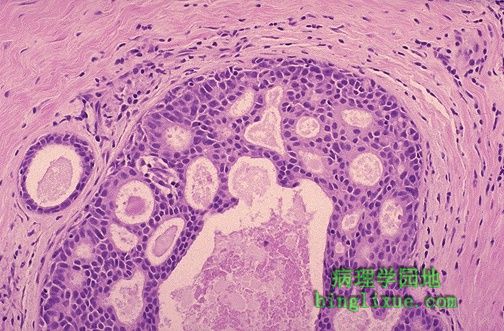 |
图示乳腺导管内癌典型的筛孔状结构。导管内的肿瘤上皮细胞表现为淡染和多型现象,但是他们有边缘锐利的孔像被切饼机切过一样。 The classic cribriform pattern of intraductal carcinoma of the breast is shown here. The neoplastic epithelial cells within the duct show minimal hyperchromatism and pleomorphism, but they have holes with sharp margins as though punched out by a cookie cutter. |
 |
粉刺癌型导管内癌,它的特征是出现快速增生高度恶性的细胞。值得注意的是导管内的显著中央坏死。 Here is a comedocarcinoma pattern of intraductal carcinoma, which is characterized by the presence of rapidly proliferating, high-grade malignant cells. Note the prominent central necrosis in the ducts. |
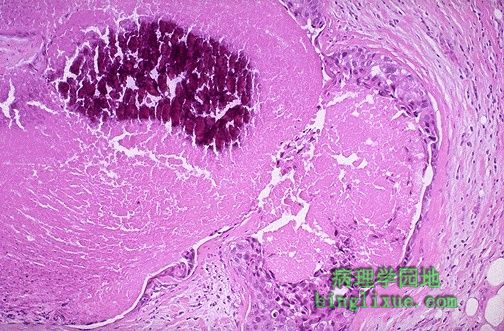 |
如图,在有粉刺癌的导管中心区细胞常为坏死性与钙化的。中央坏死导致肉眼下特征性干酪样物质受压从导管内溢出(呈粉刺样)。 The cells in the center of the ducts with comedocarcinoma are often necrotic and calcify, as shown here. This central necrosis leads to the gross characteristic of extrusion of cheesy material from the ducts with pressure (comedone-like). |
 |
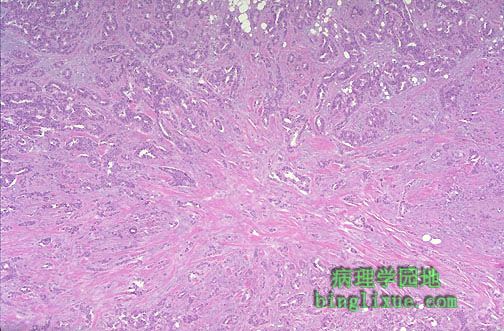
乳腺浸润性导管癌。值得注意的是不确切的腺向周围胶原间质浸润。在中心的右下部也有小的微钙化,能通过乳腺X射线造影术见到。大约65%到80%的乳腺癌为这种类型。 This is infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast. Note the infiltration of ill-defined glands into the surrounding collagenous stroma. There is also a small microcalcification at the lower right of center, a finding that could be seen by mammography. About 65 to 80% of breast cancers are of this type. |
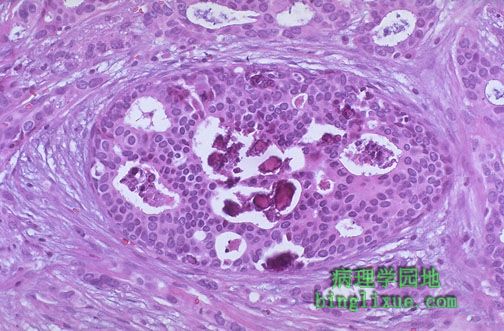 |
同时看到导管内癌与浸润性导管癌。值得注意的是中心处筛型且有明显微钙化的导管内癌组成部分。其周围是浸润性癌细胞。 Both intraductal and infiltrating ductal carcinoma are seen here. Note the intraductal component in the center with cribriform pattern and prominent microcalcifications. Surrounding this are infiltrating carcinoma cells. |
 |
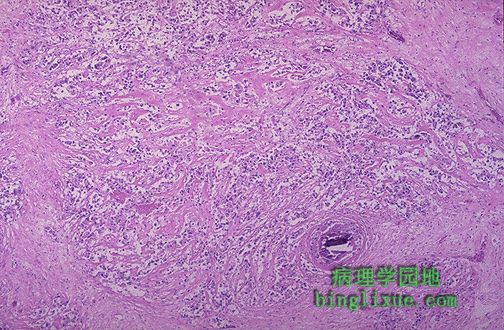
低倍放大的乳腺浸润性导管癌显示自中央区呈放射状发出的纤维组织。大量纤维组织使得肿瘤呈硬癌的硬度。这样侵袭性癌可能浸润胸壁,使其不活动。 This infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast at low magnification appears to radiate from a central area of desmoplasia. This collagenous component gives the neoplasm a hard "scirrhous" consistency that is palpable. Such an invasive carcinoma may be fixed to underlying chest wall, making it non-mobile. |
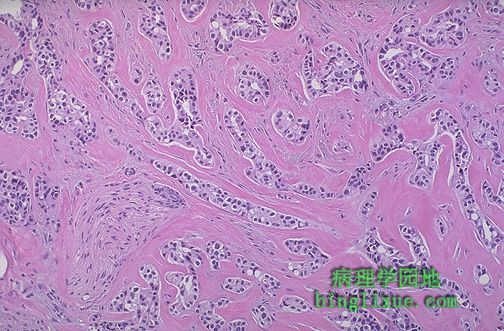 |
值得注意的是这个乳腺浸润性导管癌内的小癌巢和瘤细胞及其间明显的胶原蛋白形成的浸润性条索。致密的纤维结缔组织间质的显著增生造成了典型浸润性导管癌的特征性病变硬癌特征。注意左下方被肿瘤包围的神经。 Note the small nests and infiltrating strands of neoplastic cells with prominent bands of collagen between them in this ductal carcinoma of the breast. It is this marked increase in the dense fibrous tissue stroma that produces the characteristic hard "scirrhous" appearance of the typical infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Note the nerve surrounded by the neoplasm at the lower left. |
 |
中央为有癌细胞排列于其中的导管。然而,该导管癌不仅限于导管,还向外浸润至周围间质而成了浸润性导管癌。 In the center is a duct lined by carcinoma cells. However, this ductal carcinoma is not confined to just the duct, but infiltrates outward into the surrounding stroma as an infiltrating ductal carcinoma. |