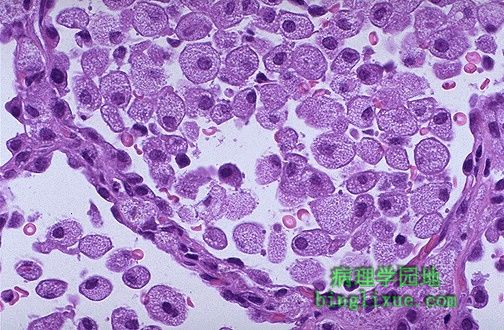
内源性类脂性肺炎,肺泡中可见大量泡沫状充满脂质的巨噬细胞。内源性是指肺和血管破裂释放脂质,通常出现在栓塞的远端(如肿瘤,吸入性异物,或支气管扩张症)。巨噬细胞聚集起来吞噬脂质。
This is the microscopic appearance of an endogenous lipid pneumonia in which numerous foamy lipid laden macrophages are present in alveolar spaces. The term endogenous refers to the origin of the lipid material from breakdown of lung and blood, usually distal to the site of an obstructive process (such as a neoplasm, an inhaled foreign body, or bronchiectasis). The macrophages collect to ingest the lipid material.

