
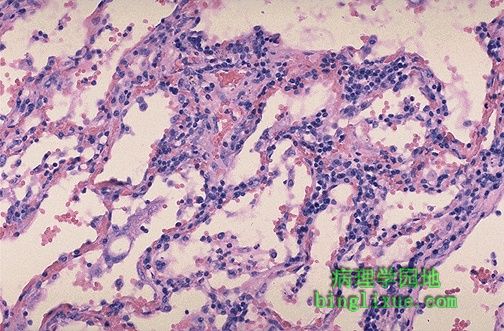
某些病因比如病毒多导致慢性炎症,如图甲型流感病毒感染者肺。慢性炎症更容易浸润组织间质,而急性炎症的渗出主要累及表面及间隙。
Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a patient with influenza A. Note also that the inflammatory infiltrates of chronic inflammation are more likely to be interstitial (within tissues) rather than exudative (above surfaces or in spaces) like acute inflammation.