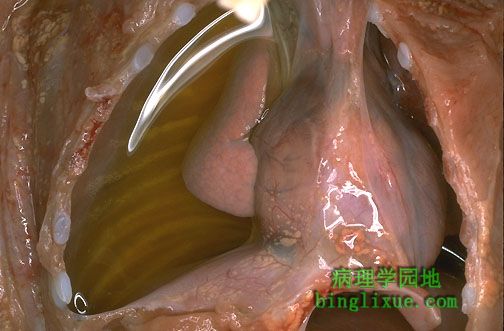
小儿胸腔积液,液体呈浅黄*色,渗出严重。
血管外液体的积聚分为以下几种类型:
渗出:渗出液中富含蛋白和/或细胞。渗出液较混浑。
漏出:属于血浆的超滤液,含有少量蛋白,极少量细胞,液体澄清。
进入体腔的液体分为以下几类:
浆液:稀薄,含少量细胞。
血性浆液:含较多红细胞。
纤维蛋白:交织的纤维蛋白源于富含蛋白的渗出液。
化脓:有大量嗜中性粒细胞,在胸膜腔积聚又称为积脓。
Here is an example of fluid collection into a body cavity, or an effusion. This is a right pleural effusion (in a baby). Note the clear, pale yellow appearance of the fluid. This is a serous effusion. Extravascular fluid collections can be classified as follows:
Exudate: extravascular fluid collection that is rich in protein and/or cells. Fluid appears grossly cloudy.
Transudate: extravascular fluid collection that is basically an ultrafiltrate of plasma with little protein and few or no cells. Fluid appears grossly clear.
Effusions into body cavities can be further described as follows:
Serous: a transudate with mainly edema fluid and few cells.
Serosanguinous: an effusion with red blood cells.
Fibrinous (serofibrinous): fibrin strands are derived from a protein-rich exudate.
Purulent: numerous PMN's are present. Also called "empyema" in the pleural space.

