
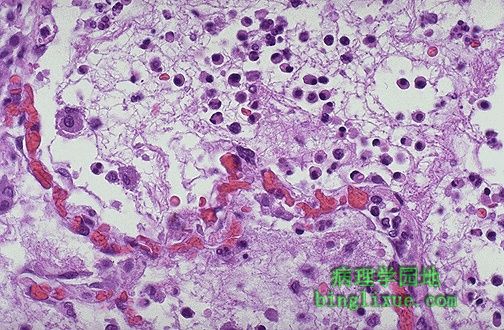
Seen here is vasodilation with exudation that has led to an outpouring of fluid with fibrin into the alveolar spaces, along with PMN's. The series of events in the process of inflammation are:
Vasodilation: leads to greater blood flow to the area of inflammation, resulting in redness and heat.
Vascular permeability: endothelial cells become "leaky" from either direct endothelial cell injury or via chemical mediators.
Exudation: fluid, proteins, red blood cells, and white blood cells escape from the intravascular space as a result of increased osmotic pressure extravascularly and increased hydrostatic pressure intravascularly。
Vascular stasis: slowing of the blood in the bloodstream with vasodilation and fluid exudation to allow chemical mediators and inflammatory cells to collect and respond to the stimulus.