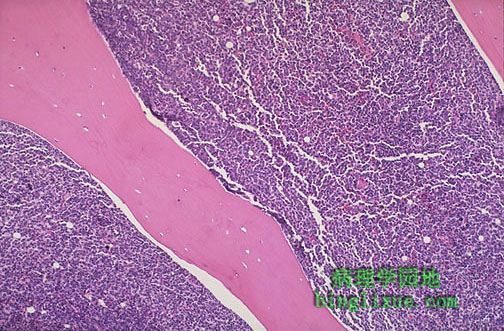
与再生障碍性贫血不同,白血病的结果是骨髓有大量细胞。如图可见粉红色的骨小梁之间的骨髓几乎100 %是细胞,是由急性淋巴母细胞性白血病(ALL)的白血病细胞构成,这些细胞实际上替代或抑制了正常的造血作用。虽然骨髓有非常多的细胞,但外周血细胞减少。这就解释了白血病的并发症感染(缺乏正常的白细胞)、出血(缺乏血小板)和、贫血(缺乏红细胞)的原因。
In contrast to aplastic anemia, leukemia results in a highly cellular marrow. The marrow between the pink bone trabeculae seen here is nearly 100% cellular, and it consists of leukemic cells of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) that have virtually replaced or suppressed normal hematopoiesis. Thus, though the marrow is quite cellular, there can be peripheral cytopenias. This explains the complications of infection (lack of normal leukocytes), hemorrhage (lack of platelets), and anemia (lack of red blood cells) that often appear with leukemia.

