
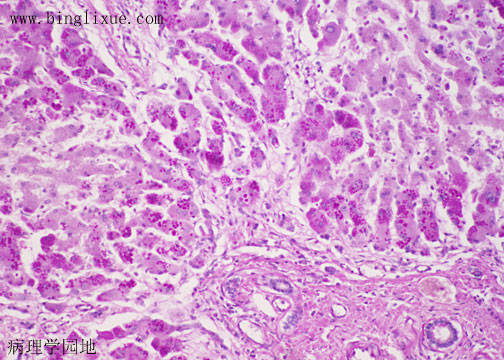
α-1抗胰蛋白酶是一种抑制蛋白酶如胰岛素活动的糖蛋白。正常的等位基因是PiM,最多见的变异型为是PiS和PiZ。异型杂合体PiMS、PiMZ有发生肝病和肺病的危险。PiZZ、PiSS和PiSZ表型病人则有更明显的危险性。α-1抗胰蛋白酶缺陷与全小叶型肺气肿有密切关系。儿童和成人也可能发生肝病。AAT病人组织学特征为肝细胞中出现小的红色圆形小体,如图所示呈PAS染色阳性。
Alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT) is a serum glycoprotein that inhibits the action of proteases such as trypsin. The normal allele is PiM; the most common mutations include PiS and PiZ. Heterozygotes PiMS and PiMZ have some risk for liver and lung disease. Patients with PiZZ, PiSS, and PiSZ are at increased risk. Deficiency of AAT has been associated with the early onset of panlobular emphysema in adults. Liver diseases in both children and adults can also occur. Children with AAT may present with neonatal hepatitis or with cirrhosis developing during the second year of life or later. Adults with AAT deficiency may have normal livers, may develop chronic active hepatitis, or may have cirrhosis. The distinctive histologic finding in cases of AAT deficiency is the presence of small round red globules in liver cells near portal tracts or fibrous septae. These globules stain strongly with PAS, as shown here, and have been shown to consists of material antigenically related to AAT. The pathogenesis of these globules and the relationship to the development of liver disease is unclear.