
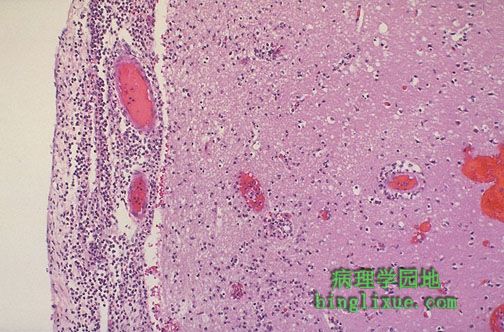
显微镜下,左侧受累的脑膜上可见嗜中性粒细胞渗出,并有明显的血管扩张。在通向右侧的皮质处有水肿和局部炎症(经由菲-罗隙向下扩展)。急性脑膜炎多为细菌感染。水肿可引起脑疝和死亡。感染的溶解可能引起粘连性蛛网膜炎,粘连性蛛网膜炎使蛛网膜下腔变小甚至消失,最后造成梗阻性脑积水。
Microscopically, a neutrophilic exudate is seen involving the meninges at the left, with prominent dilated vessels. There is edema and focal inflammation (extending down via the Virchow-Robin space) in the cortex to the right. This acute meningitis is typical for bacterial infection.This edema can lead to herniation and death. Resolution of infection may be followed by adhesive arachnoiditis with obliteration of subarachnoid space leading to obstructive hydrocephalus.