
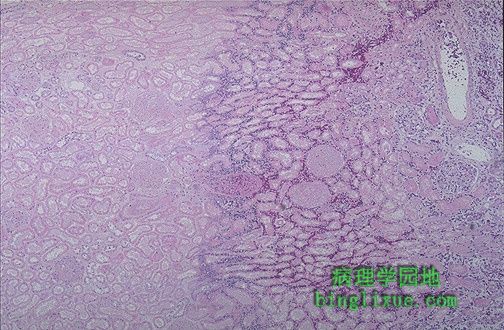
图示:凝固性坏死。镜下观:左侧的肾皮质遭受了缺氧性损伤后,细胞呈栅栏状排列。中间是细胞未完全坏死的出血带。最右侧是正常的肾实质。
Microscopically, the renal cortex has undergone anoxic injury at the left so that the cells appear pale and ghost-like. There is a hemorrhagic zone in the middle where the cells are dying or have not quite died, and then normal renal parenchyma at the far right. This is an example of coagulative necrosis.